Bonus Episode: Reflections on the Election Cycle – A Message for the Deconstruction Community
Welcome to today’s deep dive into a topic that’s been stirring within me for months. If you’re new here, let me explain the deconstruction space, or the deconstruction community—a movement that’s gaining momentum for those of us disentangling ourselves from rigid, fundamentalist beliefs. This process is supposed to be healing and, ideally, a source of growth, but it’s not without its share of controversy. That’s what we’re here to talk about.
In my podcast episode titled Faith Unbound: Navigating the Process of Disentanglement—or rather, Deconversion after my own journey took a deeper turn—I discussed my initial discovery of this space back in February. At that point, I’d begun to question my former beliefs, and the deconstruction community felt like a safe haven. After 6-7 months in, I’m seeing patterns that are unsettlingly familiar. The community has been valuable, yet I’ve grown concerned as it increasingly mirrors the same kinds of rigidity and tribalism many of us were trying to escape.
My posts and Instagram reels have hinted at this frustration, but I’m here today to pull these thoughts together more fully. Moving away from one dogma only to embrace another feels to me, like a new form of entrapment. The craving for certainty and “the right side” is strong, and without realizing it, we’re swapping one rigid system for another. In this space that’s supposed to champion open-mindedness, judgment and exclusion seem to have replaced curiosity and true critical thought.

It’s a reminder that true growth and change happen only when we’re open to different perspectives—not quick to label those who disagree with us as enemies. As the philosopher John Stuart Mill argued in his 1859 work, On Liberty, Free speech is essential for discovering the truth. He believed true understanding and truth itself emerge only through open debate and free expression. This highlights the complexity of truth, it’s only when differing perspectives clash that ideas are refined and strengthened. Let’s explore how that idea relates to today’s topic.
Setting the Stage: The Political and Psychological Landscape
Before we dig into the deconstruction community, let’s set the stage with something I found really interesting. Back before the 2024 election, journalist Mark Halperin expressed some serious concerns on Tucker Carlson’s podcast (cue the BOOs and HISSS from all the progressives–I hear you!) about what would happen if Trump were to win a second term. He predicted widespread psychological distress, especially among Democrats, which would affect everything from mental health to social interactions. And, wow, did that hit the mark.

Since Trump’s victory, movements like the 4B movement have surged among women on social media, particularly in response to reproductive rights concerns and conservative gender roles. Originating in South Korea, the movement’s name, “4B,” stems from “B,” shorthand for “no” in Korean, symbolizing “No sex, No dating, No marrying men, and No children.” Recently, the movement has sparked a 450% increase in Google searches in the U.S., with many calling it the “4 Nos” or referencing “Lysistrata” for its radical stance against traditional gender expectations. I’ve shared my thoughts on traditional gender expectations in a previous episode.

The Blue Bracelet Movement: Solidarity or Performative Gesture?
Following the 2024 election, white women supporting Kamala Harris have rallied around an unexpected symbol: a blue bracelet. For many, it represents allegiance, a small but visible way to signal “I’m not with them” to women who voted for Trump. But like other quick-fix political symbols, it’s raising questions: Does this bracelet truly contribute to progress, or is it merely performative—a way to sidestep deeper, tougher conversations within their communities?
The trend echoes past symbolic movements like 2017’s “pussy hats,” which aimed to unify and empower but were later criticized for their lack of sustained action. Today, similar critiques have emerged around the bracelet, with critics suggesting it’s more of a comforting gesture for its wearers than a true commitment to change. Some Black activists and allies have pointed out that symbols alone aren’t enough; they want allies willing to challenge and change the beliefs of those around them, including friends and family who may hold differing views.
Could the Blue Bracelet Movement become a lasting emblem of allyship or fade as a passing trend? Its fate rests on whether those wearing it step up to engage in hard conversations and meaningful action.
Misinformation and Its Impact on Abortion Laws
But let’s get back to deconstruction—and something that’s been coming up a lot lately, particularly within that space: misinformation about abortion laws. Here’s the thing: there is no federal abortion ban in place. I repeat, NO federal abortion ban.
The Trump administration’s role in the overturning of Roe v. Wade has sparked fierce debates on both sides, but it’s important to clarify that the administration never stated it aimed to eliminate abortion nationwide. Instead, the ruling simply returned the power to regulate abortion to individual states. Some conservative figures have even used quotes from Ruth Bader Ginsburg to suggest she supported a more gradual, state-based approach. However, Ginsburg critiqued the federal approach, arguing a more state-focused shift could have garnered broader public support for gender equality. Polls consistently show that while many Americans support the legality of abortion, most also favor restrictions—especially in later stages of pregnancy. This nuance, however, often gets lost in campaign rhetoric, which is typically framed in absolute terms to galvanize voter turnout. But as we’ve seen, such messaging has not always yielded the intended results, revealing the complexity of public opinion on this issue.
Yes, the Roe v. Wade decision was overturned, but all that did was give states the power to regulate abortion. Some states have restrictions, sure, but no federal law is imposing a nationwide ban. And without a massive shift in Congress and the courts, it’s unlikely that will happen.
I don’t think it will. Trump himself has spoken out against that. His wife has spoken for protecting these in some way, shape or form. We have other folks coming over from the Democratic Party under this Unity Party bracket. I just don’t think that they’re going to force Christian nationalism, and abortion bans across the entire nation. I guess we’ll see.
Then, there’s this idea going around that women won’t be able to access life-saving procedures if they have a miscarriage. This is just false. In fact, most states with abortion restrictions still allow medical treatments for miscarriages, like dilation and curettage (D&C), which are essential to protect a woman’s health. What’s actually being restricted are elective abortions—not necessary procedures.
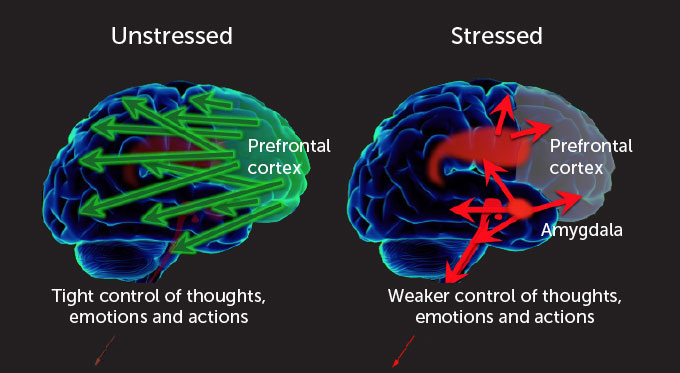
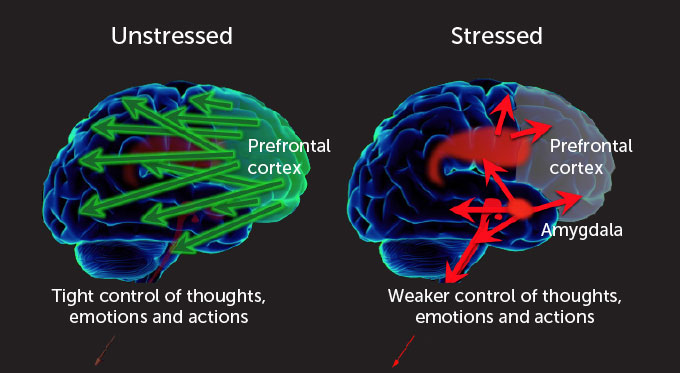
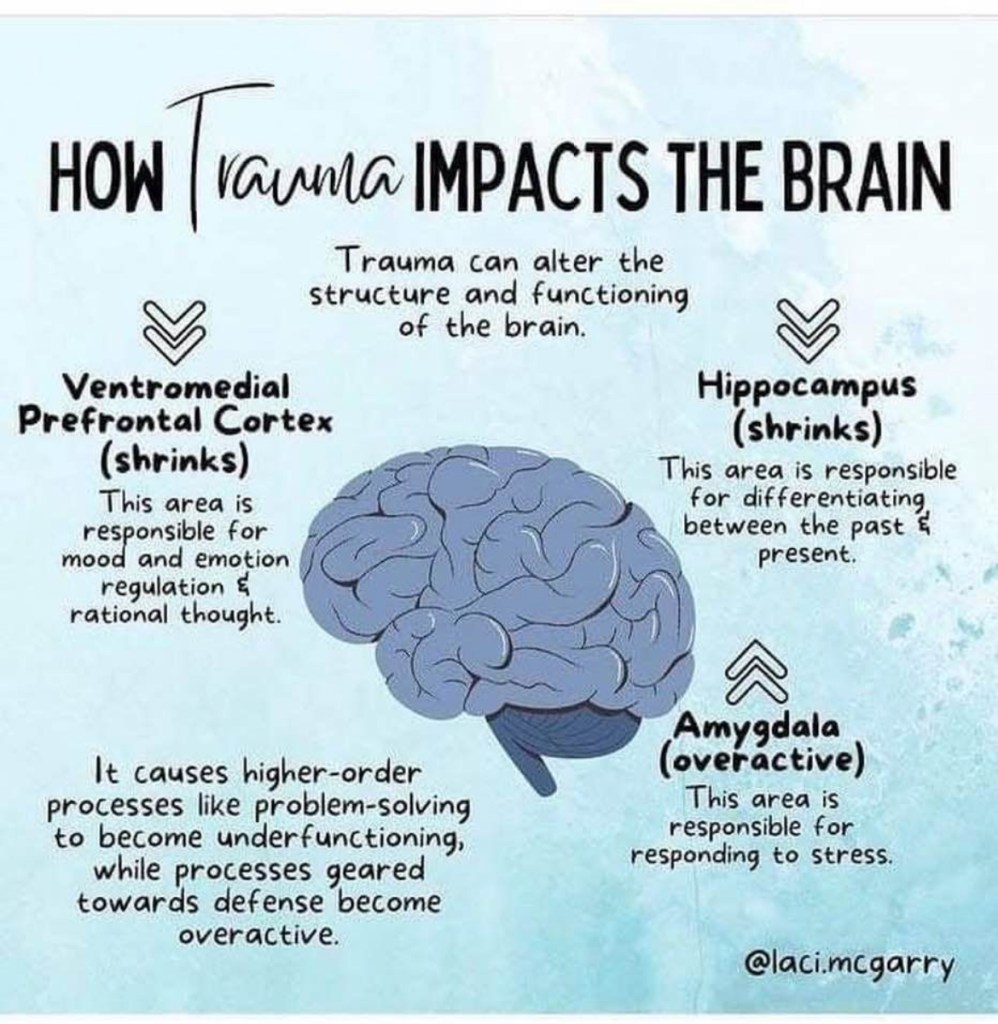
But here’s where things get really tricky. The spread of these exaggerated claims taps into the emotional centers of our brains. If you remember our previous episodes, we talked about amygdala hijacking—the brain’s response to fear and anxiety. When we hear these alarmist claims, it triggers that fear-based reaction, shutting down our ability to think rationally. Instead of focusing on the facts, we’re just reacting emotionally.
The Dangers of Misinformation
Let’s talk about the danger of this. Misinformation, especially when it involves highly emotional issues like reproductive rights, isn’t just harmless chatter—it’s psychological warfare. It keeps people in a constant state of anxiety, preventing them from thinking rationally. The real issue? People are more likely to believe in the fear-based narrative than to actually check the facts. They’re too busy being triggered emotionally.

This plays directly into the hands of the fearmongers. It becomes easier to control a population if you can make them afraid, right? And what do we see happening? Misguided campaigns around “miscarriage care,” the spread of exaggerated stories, and people feeling like their rights are under direct attack. It’s chaos. And it’s all based on misinformation, yet the ones who are screaming the loudest about misinformation are the very ones spreading it.
Can you already hear the echoes of evangelicalism? This brings me to the concepts of Jonathan Haidt’s the Righteous Mind: Why Good People Are Divided by Politics and Religion because they apply here. Haidt explains how our moral intuitions drive our beliefs and politics, often dividing us along different moral foundations.
Many folks in the deconstruction space, now lean left, where values like care and fairness are paramount. Meanwhile, conservative values like loyalty and authority are often viewed as suspect, fostering an “us vs. them” mentality that can feel righteous but alienating. Ironically, in striving for freedom and empathy, the deconstruction space sometimes ends up falling into the same black-and-white thinking it critiques.
In tandem, Greg Lukianoff and Jonathan Haidt’s book The Coddling of the American Mind offers a useful framework for understanding these shifts, identifying “Three Great Untruths”: 1) “What doesn’t kill you makes you weaker,” 2) “Always trust your feelings,” and 3) “Life is a battle between good people and evil people.” These untruths, they argue, create fragility, discourage critical thinking, and foster a tribal mentality—traits that increasingly characterize the deconstruction space and parts of the progressive left.
It’s ironic to me that some people leave evangelical Christianity thinking they’re free, only to stumble into a new form of dogma within the deconstruction space. My experience is different—I didn’t grow up in the church but was recruited during the pandemic. Having lived outside of purity culture, I feel fortunate not to carry that baggage. While I empathize with those navigating their journeys, it’s tough to see them act as critics and bullies. Let’s unpack these dynamics by exploring three key untruths in this space.
1. The Untruth of Fragility: “What doesn’t kill you makes you weaker.”
For many, deconstructing from fundamentalist beliefs took resilience and a willingness to confront discomfort. Yet, in today’s deconstruction space, there’s an emphasis on avoiding ideas seen as “unsafe” or “harmful”—typically anything that deviates from progressive orthodoxy. and I mean, I genuinely felt this way. I think that might be somewhat of a trauma response. I was like, I hate the patriarchy. I must stand up against this. This is harmful. This is dangerous. And there is a lot of data proving that this isn’t true, whether we want to look at the history of the ancient church or just, you know, the research data that I’ve shared in previous episodes but my point–this fragility, reinforced by social media algorithms, cultivates an environment where disagreement feels threatening rather than enriching.
This approach mirrors the fundamentalist rejection of “dangerous” secular ideas, where dissent is demonized. The irony is that what began as a call for open-mindedness has become a kind of brittle certitude, one that isolates rather than connects. Instead of learning resilience, we’re re-teaching fragility, limiting our growth and deepening the ideological chasm.

2. The Untruth of Emotional Reasoning: “Always trust your feelings.”
Fundamentalism often equates strong feelings with truth—“If I feel it, it must be right.” In the deconstruction space, there’s a similar emphasis on emotional reasoning. If something feels offensive or unsettling, it’s treated as harmful. This approach is amplified by social media, where outrage and personal offense are rewarded with visibility.
Haidt’s work reminds us that emotions shape our moral judgments but don’t always lead to truth. Reacting purely on feeling closes off critical thinking, creating echo chambers where alternative perspectives are rarely considered. Instead of fostering deeper understanding, emotional reasoning entrenches our biases, fueling judgment rather than curiosity.
3. The Untruth of Us vs. Them: “Life is a battle between good people and evil people.”
The most divisive untruth is the idea that the world can be split into “good” and “evil” camps. This is evident in how some in the deconstruction community approach politics and social issues, painting conservatives or moderates as morally inferior. We see a rigid, “with us or against us” mentality, where anyone who questions progressive narratives is labeled “deplorable,” “harmful,” “Trash”, “Nazi” or worse.
Haidt’s research reveals that moral division is natural; we all tend to view those who disagree with us as misguided or even morally flawed. But when we approach every difference as a moral battleground, we close off true dialogue. Coming from a high-Calvinist church—one of the most cult-like, fundamentalist circles you can get into—I know what it’s like to think the rapture is imminent or to believe that if you don’t say all the “right” words exactly, you’ll burn in hell. My journey has taken me from being pro-choice in Portland, OR, having had three abortions myself, to joining an abolitionist movement to outlaw abortion. I haven’t even spoken about the profound pain and regret I carry about this. Yet here I am, reflecting on how divisive our society has become, with so little room for understanding across political lines. In the deconstruction space, you’d expect a shared empathy after leaving behind rigid belief systems, but instead, the culture seems to mirror the very exclusivity and “us vs. them” mentality of evangelical spaces.
Living in Portland, surrounded by ideologies that often pushed the limits of what I felt was morally comfortable, I wrestled with the impacts of various movements. I started to question whether certain messages of empowerment—like third-wave feminism—truly uplift or, instead, encourage behaviors that commodify women’s bodies and promote sexualization from a very young age. And while sex work has become a celebrated concept under the mantra “sex work is real work,” my own painful experiences in that industry make me see things differently. To me, it’s not empowering; it’s the opposite. Instead of championing it, I believe we should work to dismantle the industry.
It’s not just isolated concepts; there’s a broader pattern of glorifying “anything goes” hedonism and dismissing traditional values in the progressive space, which I find deeply troubling. Living in that environment left me with a raw understanding of how damaging these ideologies can be, leaving permanent scars. I grieve over the three abortions I’ve had. I cry because, despite being told it was just “a clump of cells,” I knew it was more than that. Watching the left demand “trust the science” while denying that life begins at conception feels twisted to me.
Moreover, there’s a deep, dark history in the advocacy of reproductive rights that gets glossed over—like the disturbing eugenics past of Planned Parenthood’s Margaret Sanger. Are we just going to ignore that?
Since the last election ended with a Trump landslide victory, rather than sparking any self-reflection, this moral absolutism seems to have intensified. The comments sections on many deconstruction accounts reveal the same tribal thinking they claim to oppose. Instead of creating bridges, we see entrenched sides, instead of open-mindedness, we see judgment.
Look, I’ve been there. I was a proud Democrat in the past. I voted for Obama. But now, as an independent, I’m calling it like I see it. Democrats need to take a good hard look at themselves if they want a chance at victory. Blaming the electorate isn’t the answer. You cannot keep denying biology and pretending men. Along in women’s sports, restrooms or prisons. The idea that kids should undergo irreversible changes. It’s misguided and is absolutely out of touch. The open border agenda. It’s hurting American workers, pushing down wages and driving up the cost of housing. When will you start protecting your own people instead of pandering to these extreme policies? Discriminating against whites, Asians and men and the name of countering past wrongs is not only setting us back, but it’s racist in itself. Abandoning merit-based selection is wrecking our economy and opportunities for everyone. I mean, you cannot let people camp, defecate and shoot up in public spaces and expect things to improve. The average voter is seeing all of this and they’re rejecting it. If Democrats want to win again, they need to rethink their approach and get back to reality. Enough is enough.
The Pipeline Problem: How Social Media Radicalizes
This divide is worsened by social media, where algorithms favor outrage and tribalism, pulling people toward extreme ideologies. Just as researchers have observed a “crunchy hippie to alt-right pipeline,” there’s a similar dynamic at play in progressive spaces, where folks in the deconstruction space are drawn into radical social justice ideologies that feel every bit as dogmatic as evangelicalism.
In this progressive pipeline, identity politics becomes a weapon, and moral purity is enforced through a power/victim binary that discourages complexity and invites fear of being labeled an oppressor. This kind of ideological purity resembles the control and certainty we experienced in evangelicalism, only now with a new political coat of paint.

And this leads me into the horseshoe theory suggests that the far-left and far-right, though seemingly at opposite ends of the spectrum, often mirror each other in attitudes and tactics. This theory, initially presented by French philosopher Jean-Pierre Faye, proposes that the extremes of any ideology may end up behaving similarly—both tending toward authoritarianism and totalitarian thought despite their stated differences. Although this theory has its critics, the broader concept of ideological mirroring holds up in our analysis of what’s happening in the deconstruction space. At first, it was all about freedom—breaking away from oppressive systems, rejecting dogma, and embracing openness. But ironically, as people deconstruct their faith, they can fall into a similar trap: from being free thinkers to members of a new ideological cult.
Basically, when you leave fundamentalism without fully deconstructing dogmatic thinking, you risk trading one rigid ideology for another. Without cultivating humility and empathy, we will perpetrate the very same cycles of judgement and exclusion.
The Path Forward: True Openness and Curiosity
What’s the solution here? Jonathan Haidt’s insights remind us that real dialogue begins by understanding the values behind other people’s beliefs, even if we disagree with them. Progress and healing require that we listen beyond the labels, engaging in good faith rather than moral grandstanding. If we are to avoid replicating the very structures we’re deconstructing, we need to make space for differing perspectives and approach them with curiosity.
So, this means you cannot demonize conservatives, you cannot call everyone that voted for Trump a bigot, racist, misogynist. There’s something wrong with that thinking. You have been sold these three untruths. It’s a tired accusation that doesn’t hold up when you look at the numbers. Trump support among white voters did drop from 57% in 2020 to 49% in 2024. But the kicker is his support among black and Latino voters actually went up from 38 to 42%. So, against all odds, Trump is doing something that the Democratic Party has failed to do for decades. He’s making the Republican Party more diverse than has been in 60 years. Let’s cut out the divisive name calling and start acknowledging the reality of his growing appeal across different communities.
Real change happens when we go beyond just labeling others and instead build spaces where critical thought can flourish—even when it’s uncomfortable. This is my message to the deconstruction community and beyond!
It’s simple: stop pretending that we have all the answers. True freedom of thought is not about certainty. It’s about curiosity. It’s about asking the tough questions, not just parroting whatever’s trendy on social media or echoing the louder voices in your ideological group.
We need to do away with the binary thinking that divides us into “good” or “evil,” “us” or “them,” and start embracing true diversity of thought. Only by having those uncomfortable, nuanced conversations will we ever break free from the ideological cults—whether they’re rooted in religion, politics, or even deconstruction itself.
So, as we wrap up today’s episode, remember this: It’s time to get real. Misinformation is everywhere, and sometimes, it’s coming from the very people who claim to be fighting it. Whether it’s the left, the right, or the deconstruction space—don’t get caught up in the hype.
Thanks for tuning in to Taste of Truth Tuesdays. Until next time, keep questioning, keep learning, and never, ever stop thinking for yourself.