Welcome to Taste of Truth Tuesdays, where we unravel the strange, the mysterious, and today—the terrifying. This post delves into one of history’s darkest chapters: the witch hunts. We’ll explore how fear, superstition, and control shaped centuries of persecution and how these patterns are still evident in the modern world. Witch hunts aren’t just a thing of the past—they’ve evolved.
The European Witch Hunts – Early Modern Europe
Let’s start in early modern Europe. Scholar Peter Maxwell-Stuart illuminates the rise of demonology, where the fear of magic and the devil became a weapon of control for those in power. Beginning in the 1500s, political and religious leaders manipulated entire populations by tapping into their deep-rooted fears of ‘evil forces.’ The Church, in particular, weaponized these beliefs, positioning itself as the protector against witches—women (and sometimes men) believed to consort with devils or conjure dark forces. As the idea took hold that witches could be behind every famine, illness, or death, this created a perfect storm of paranoia.

Stuart argues that demonology texts—many sanctioned by the Church—fueled mass hysteria, feeding the narrative that witches were not just local troublemakers but cosmic agents of Satan, hell-bent on destroying Christendom. Ordinary people lived in constant fear of betrayal by their neighbors, leading to accusations that could swiftly escalate into brutal trials, with the accused often tortured into confessing their ‘diabolical’ crimes.
To understand how demonology in Europe gained such traction, we need to go back to Augustine of Hippo. We have mentioned him before in previous episodes, whose writings in the 4th and 5th centuries laid the foundation for Christian perceptions of the devil and demons. Augustine’s ideas, especially in City of God, emphasized the constant spiritual warfare between good and evil, casting demons as agents of Satan working tirelessly to undermine God’s plan. He argued that humans were caught in this cosmic battle, susceptible to the devil’s temptations and tricks.

Augustine’s Doctrine of Demons
According to Augustine, demons were fallen angels who had rebelled and now sought to deceive and destroy humanity. While Augustine didn’t explicitly discuss witches, his interpretation of demons helped fuel the belief that humans could be manipulated by evil spirits—whether through pacts, possession, or magical practices. This idea later influenced medieval and early modern European demonology.

Augustine’s views on original sin—that humanity is inherently flawed and in need of salvation—also intensified fears that people, especially women (who were seen as ‘weaker’ spiritually), were more vulnerable to the devil’s influence.
SIDE NOTE: We have discussed the theological concept of original sin in previous episodes: Franciscan wisdom navigating spiritual growth and challenges with Carrie Moore, we specifically spun the doctrine of original sin on its head and then also Unpacking Religious Trauma: Navigating the Dynamics of Faith Deconstruction with Doctor Mark Karris.
In the centuries that followed, these ideas were weaponized to justify witch hunts. Augustine’s legacy is evident in how later theologians and demonologists, such as Heinrich Kramer (author of the infamous Malleus Maleficarum), built upon his ideas of demonic interference to condemn witchcraft as a real, existential threat to Christian society.
Maxwell-Stuart reveals that the creation of demonology wasn’t just religious but deeply political. Kings and clergy alike realized they could consolidate power by stoking the flames of fear, casting witches and sorcerers as a common enemy. The trials served a dual purpose: they reinforced the Church’s supremacy over the spiritual realm and gave ruling elites a tool for maintaining social order. Accusing someone of witchcraft was an effective way to silence dissent or settle personal scores.
Fear as a Tool of Control
Fear wasn’t just manufactured by rulers—it was deeply ingrained in the societal, religious, and legal systems of the time. Scholar Sophie Page reveals how beliefs in magic and the supernatural were not fringe ideas but core components of medieval and early modern life. Magic wasn’t merely a mysterious force; it was a pervasive explanation for any calamity. Failed harvests, plagues, or unexplained illnesses were often attributed to witches or the devil, creating a society constantly on edge, where supernatural forces were believed to lurk behind every misfortune.
By embedding these beliefs into legal codes, authorities could target suspected witches or sorcerers under the guise of protecting the community. Page’s work illustrates how rituals once seen as protective or healing gradually became demonized. Harmless folk practices and herbal remedies, used for centuries, began to be recast as witchcraft, especially when things went wrong. People, particularly those in rural areas, were vulnerable to this thinking because religion and superstition were inseparable from daily life.
Partisan scholars have long debated whether Catholics or Protestants were the “real” witch hunters, but they’ve made little headway. One important change in Christian morality, as discussed by John Bossie, occurred between the 14th and 16th centuries. The moral focus shifted from the Seven Deadly Sins—pride, greed, lust, envy, gluttony, anger, and sloth—to the Ten Commandments. This change, influenced by reform movements that shaped the Protestant Reformation, prioritized sins against God over those against the community. Idolatry and the worship of false gods became viewed as the gravest offenses.

This redefinition of witchcraft followed suit. Instead of being seen as harmful actions toward neighbors, witchcraft was now linked directly to devil worship and regarded as serious heresy. Scholars and church leaders began merging various forms of folk magic and healing into this new narrative, suggesting that practitioners were either knowingly or unknowingly making deals with the devil. Confessions of pacts or attendance at “witch gatherings” were shaped to highlight community failings, like envy and resentment. Consequently, educated society began to see witchcraft as a real threat rather than mere superstition. While traditional beliefs about magic still existed, they were overshadowed by fears of violent backlash from reformers.
The Power of Dualistic Thinking
This dualistic thinking, influenced by St. Augustine, gave rise to a semi-Manichean worldview, where the struggle between good and evil became more pronounced. Manichaeism, an ancient belief system, viewed the world as a battleground between equal forces of good and evil. Although orthodox Christianity rejected this dualism, the focus on the devil’s role in everyday life blurred those lines for many people. By emphasizing the devil’s pervasive influence, religious leaders inadvertently created a belief system in which evil seemed as powerful as good.

In this semi-Manichean view, the devil was not just a tempter of individuals but a corrupting force within communities and even within political and religious practices deemed heretical. Fears of devil-worshipping conspiracies became intertwined with anxieties about witchcraft and moral decay. Reformers, particularly in Protestant movements, fueled these fears by branding idolatry, Catholic rituals, and even folk healing as dangerous openings for the devil’s influence. This perspective transformed witchcraft from a local issue into a broader threat against God and society.
The result was a potent mix of dualistic thinking and an intense focus on spiritual warfare. This not only intensified the persecution of supposed witches but also reinforced the obsession with eliminating anything considered “satanic.” The ideological shift redefined witchcraft as a communal danger, turning innocent healing practices into accusations of demonic pacts.

Every village had its own ‘cunning folk’—individuals skilled in healing and folk magic—yet these very people could easily become scapegoats when something went wrong. The legal structures played a vital role in perpetuating this cycle of fear. Church courts, bolstered by theologians and demonologists, were empowered to try individuals accused of witchcraft, and the accusations quickly spiraled into mass hysteria. Trials often relied on tortured confessions, reinforcing the belief that witches and the devil were real and tangible threats to society. This institutionalized paranoia was a perfect storm of religion, fear, and control.
The Rise of Organized Witch Hunts
Beginning in the late 15th century, witch trials escalated into full-blown hunts, particularly after the publication of the Malleus Maleficarum in 1487. This infamous witch-hunting manual, written by Heinrich Kramer and endorsed by the Pope, offered legal and theological justifications for hunting down witches. It encouraged harsh interrogations and set guidelines for identifying witches based on superficial evidence like birthmarks, behaviors, and confessions extracted under torture. The legal system, which had already started to turn against folk healers, now had a codified method for persecuting them.
In regions like Germany, Scotland, and Switzerland, these legal trials turned into widespread witch hunts. Hundreds, even thousands, of individuals—predominantly women—were accused and executed. What’s particularly fascinating is that these witch hunts often peaked during periods of societal or economic instability when fear and uncertainty made people more susceptible to attributing their misfortunes to external, supernatural forces.
By institutionalizing the persecution of witches, rulers and religious leaders could manage social unrest and solidify their authority. The trials often reinforced the power structures by demonstrating that anyone perceived as a threat to societal order—whether through suspected witchcraft or merely social nonconformity—could be eradicated.

Witch Hunts and Gender
The scapegoating of women played a crucial role in these witch hunts. Owen Davies’ work reveals how the demonization of witches intersected with misogyny, turning the hunts into a gendered form of control. Midwives, healers, or outspoken women were more likely to be targeted, reinforcing patriarchal authority. The very skills that had once been valued, such as healing and midwifery, were redefined as dangerous and linked to dark powers.
As witch hunts spread, the legal frameworks across Europe became more refined and institutionalized, creating a climate where fear of witches and demonic possession became the norm. The trials’ obsession with confessions—often coerced under brutal conditions—further fueled public paranoia, as the more people confessed to witchcraft, the more tangible the ‘threat’ seemed.
The Modern Echoes of Witch Hunts
Fast forward to today, and we find that the legacy of witch hunts lingers. The tactics of fear-mongering, scapegoating, and social control can still be observed in modern contexts. Contemporary movements often mirror historical witch hunts, targeting marginalized groups through accusations and public shaming. Just as witch hunts flourished in times of societal uncertainty, modern societies can succumb to similar dynamics.

In the age of social media, legal accusations spread like wildfire, and the court of public opinion often acts faster than the courts themselves. Political enemies are dragged through the mud with allegations that may or may not have a basis in fact.

The case of Michael Jackson serves as a poignant example of how media narratives can distort reality. The beloved pop icon faced multiple allegations of child molestation, with the most notable case occurring in 2005 during a highly publicized trial. Accusers claimed that Jackson had abused them, yet the defense presented compelling counterarguments, including challenges to the credibility of the witnesses and highlighting inconsistencies in their testimonies. After a lengthy trial, Jackson was acquitted of all charges, but the media frenzy surrounding the case fueled public debate and sensationalism, earning him the derogatory nickname “Wacko Jacko.” This smear campaign perpetuated false narratives about his character and actions. Behind the scenes, Jackson was embroiled in a lawsuit against Sony Music, a battle he was reportedly winning at the time of these allegations. Furthermore, his controversial doctor, Conrad Murray, who administered drugs to Jackson, faced serious legal consequences for his role in the singer’s death, including manslaughter charges. The intersection of these legal battles and the media frenzy created a complex narrative that ultimately tarnished Jackson’s legacy, and that’s what truly breaks my heart.
By the time these individuals have the chance to clear their names, their reputations—and often their careers—are already in ruins. Davies’ research shows us that while modern witch hunts don’t involve burning at the stake, they do involve trial by media and mob justice.

And we can’t talk about modern-day witch hunts without bringing the CIA into the conversation. Since its inception, the CIA has been at the heart of international political manipulations—using covert methods to shape public perception, interfere in foreign governments, and even influence elections here in the United States. In the 1960s, the agency coined the term ‘conspiracy theorist’ to discredit anyone who questioned the official narratives surrounding events like the assassination of JFK. Those who didn’t toe the line were labeled as ‘paranoid’ or ‘dangerous.’ It was the modern version of labeling someone a witch—turning them into a social outcast, not to be trusted.
Fast forward to today: we see similar tactics used against whistleblowers, journalists, and activists who challenge the powerful. Think about Edward Snowden, Julian Assange, and even political figures targeted by intelligence communities. The second they start exposing uncomfortable truths, they are vilified. Whether through leaks, smear campaigns, or selective legal action, these modern-day ‘witches’ face an onslaught of accusations, designed to discredit them before they can fully tell their story.

In many cases, the evidence behind these accusations is shaky at best. The CIA’s involvement in manipulating public perception goes all the way back to Operation Mockingbird, a secret program to influence media narratives, which showed that controlling information was one of the most powerful tools they had. During the Cold War, the United States engaged in a concerted effort to influence and control media narratives to align with its interests, which involved recruiting journalists and establishing relationships with major media outlets.
Edward Bernays, often referred to as the father of public relations, played a pivotal role in these discussions on media manipulation. Working with several major companies, including Procter & Gamble, General Electric, and the American Tobacco Company, Bernays was instrumental in promoting the cigarette brand Lucky Strike, famously linking it to the women’s liberation movement. His connections extend to notable figures like Sigmund Freud, who was Bernays’ uncle, Freud’s psychoanalytic theories significantly shaped Bernays’ PR strategies. Throughout his career, Bernays leveraged media to influence public perception and political leaders, raising profound questions about the power dynamics of media and its capacity to shape societal narratives. (If you’re intrigued by the intricate interplay of media and propaganda, this is a rabbit hole worth exploring!)
Today, that same fear-mongering tactic is played out on a much larger scale. Accusations, whether of conspiracy, treason, or subversion, become tools to silence anyone questioning the status quo. Just as witches in the past were seen as ‘different’ and thus dangerous, today’s targets are often people who challenge the system.
And while throughout the 1300-1600s, there was no due process for the accused witches, today, we see something similar in the digital realm. There’s no real accountability or fairness in the court of public opinion. All it takes is a viral accusation—a tweet, a blog post, or a video—and the person’s career, family, and mental health can be obliterated overnight. No evidence required, no trial, no defense.

So, what can we learn from this history? From the witch hunts of early modern Europe to today’s viral accusations and political fearmongering, there’s one key lesson: fear remains one of the most dangerous tools of control. When we allow fear to dictate our actions—whether it’s fear of witches, outsiders, or anyone who doesn’t fit into the mold—we lose sight of reason and humanity.
In closing, I’d like to examine the phenomenon of witch hunts through the lens of amygdala hijacking, a topic we discussed in a previous episode. This term refers to the brain’s immediate response to perceived threats, where the amygdala—the emotional center of the brain—takes control, often resulting in irrational and impulsive actions.
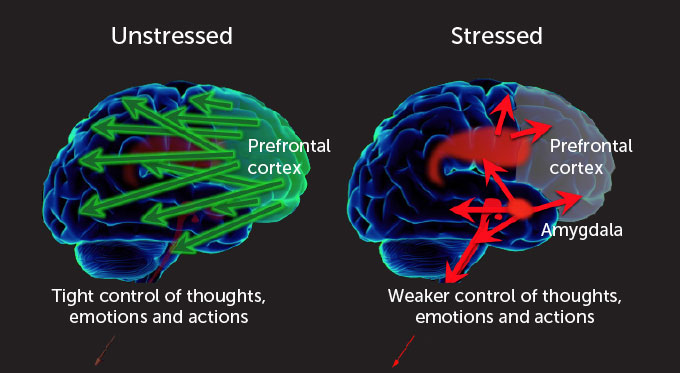
During the witch hunts, communities gripped by fear of the unknown succumbed to a mob mentality whenever someone fell ill or misfortune struck. The amygdala triggered a fight-or-flight response, compelling individuals to find scapegoats, with cunning folk and those deviating from societal norms becoming prime targets. As accusations spiraled, fear dominated decision-making instead of rational thought. Today, we observe similar patterns in how social media can incite panic, leading to modern witch hunts. When fear takes over, reason often fades, resulting in unjust vilification—echoing the dark lessons of history.
As we navigate our modern world, let’s remain vigilant against the echoes of this history, seeking truth and questioning the narratives that shape our beliefs. Fear may be powerful, but curiosity and critical thinking are our greatest allies in maintaining our autonomy and humanity.
Resources:
Briggs, Robin. Witches and Neighbors: The Social and Cultural Context of European Witchcraft. Oxford University Press, 1996.
- This book provides a comprehensive exploration of the social dynamics surrounding witch hunts in early modern Europe, highlighting the interplay of fear, community, and cultural beliefs.
Maxwell-Stuart, Peter G.Witchcraft in Europe, 1100-1700: A Sourcebook. Palgrave Macmillan, 2010.
- This sourcebook compiles essential documents related to the history of witchcraft in Europe, providing insights into how fear and persecution were constructed and justified.
Page, Sophie.Magic in the Middle Ages. Cambridge University Press, 2005.
- This book offers an analysis of the cultural and religious practices surrounding magic during the medieval period, emphasizing how these beliefs shaped societal attitudes toward witchcraft.
Bossy, John.Christianity in the West, 1400-1700. Oxford University Press, 1985.
- Bossy examines the transformation of Christian morality during the Reformation, providing context for the changing perceptions of witchcraft and heresy.
Davies, Owen. Popular Magic: Cunning Folk in English History. Continuum, 2007.
- This work explores the role of cunning folk—those who practiced folk magic—and how their practices were perceived within the broader context of witchcraft accusations.
Baroja, J. C. Witches and Witchcraft. University of California Press, 1990.
- Baroja’s work examines the historical and cultural significance of witchcraft, providing insights into the social conditions that fueled witch hunts and the cultural implications of these beliefs.