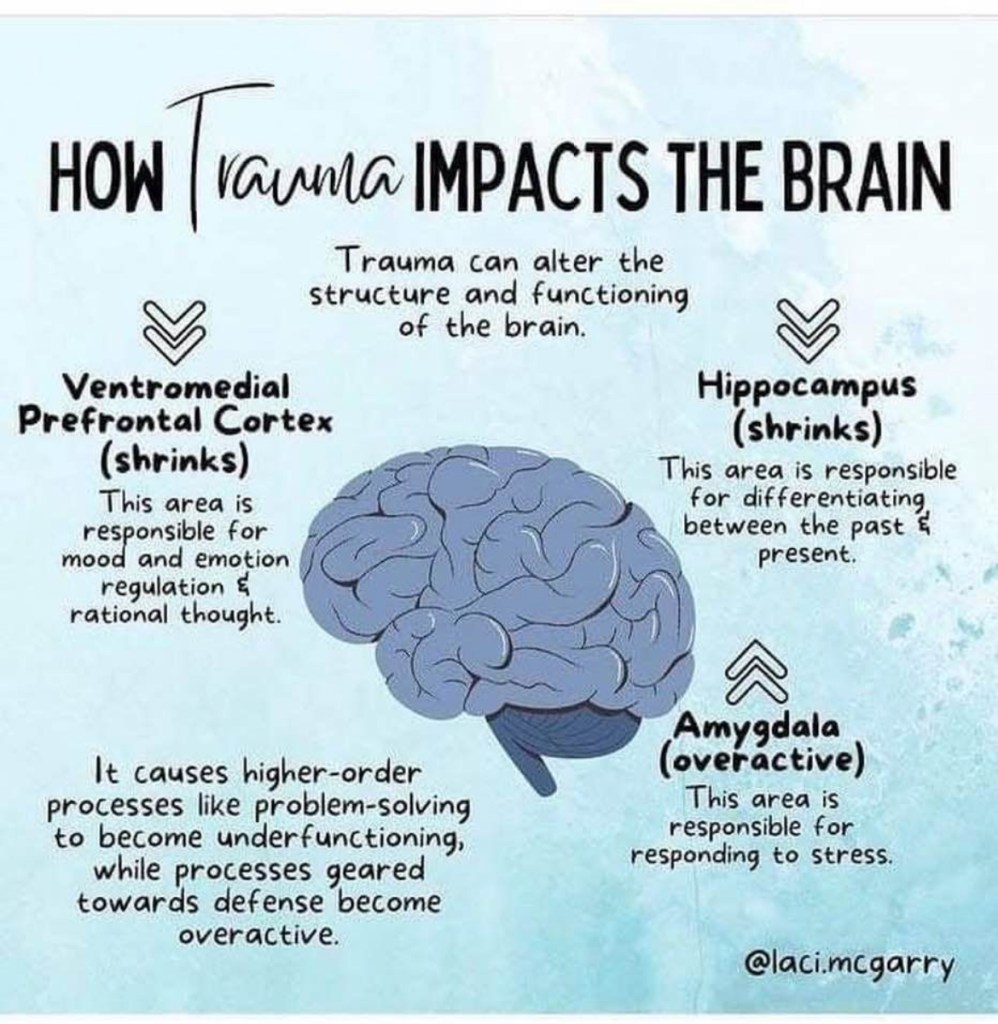
The late 19th and early 20th centuries were a time of profound change, a period when the boundaries between science, religion, and society were continually reshaped. This era saw the emergence of groundbreaking technological innovations, the rise of new belief systems, and the popularization of ideas that were once considered fringe. These developments didn’t just redefine technological progress—they also deeply influenced the way people understood the world and their place in it. Let’s explore some of the key transformations that marked this fascinating period.
🏭 An Era of Transformation

The Second Industrial Revolution: Shaping the Modern World
The Second Industrial Revolution, which spanned from the late 19th to the early 20th century, was a time of explosive growth and innovation. The advent of new technologies and processes fundamentally changed industries and daily life. Key advancements included:
- Steel Production: The Bessemer process revolutionized steel production, making it faster and more cost-effective. This development laid the groundwork for the expansion of railways, the construction of skyscrapers, and the growth of cities.
- Electric Power: The introduction of electric lighting and power systems transformed urban landscapes, extending work hours and improving the quality of life in cities. Innovations in electrical engineering also paved the way for the modern electronics industry.
- Mechanized Production: The rise of large-scale factories and mechanized production processes changed the face of manufacturing. These innovations increased productivity and lowered costs, contributing to the mass production of goods and the rise of consumer culture.

The Second Great Awakening: A Religious Revival with Social Impact
Running parallel to technological advancements was the Second Great Awakening, a religious revival movement that swept across the United States in the early 19th century. This movement was characterized by fervent enthusiasm, emotional sermons, and mass conversions. Key aspects include:
- Personal Salvation: Leaders like Charles Finney emphasized personal salvation and a direct, emotional connection with God. This focus on individual spirituality led to the growth of various Christian denominations and movements.
- Social Reform: The revivalist spirit of the Second Great Awakening also fueled social reform movements, including abolitionism, temperance, and women’s rights. Religious fervor became a driving force behind efforts to reshape society according to Christian principles.
The Intersection of Science and Religion

The Birth of the Scientist: A New Approach to Understanding the World
The term “scientist” was first coined by philosopher William Whewell in 1833, marking a significant shift in how knowledge was pursued. This period saw the establishment of scientific societies and the professionalization of research, laying the foundation for modern science. Key developments included:
- Systematic Inquiry: The emergence of the “scientist” as a distinct profession reflected a growing commitment to systematic, empirical methods for understanding the natural world. This approach contrasted with earlier, more philosophical or speculative methods of inquiry.
- Scientific Societies: The formation of scientific societies provided a platform for the exchange of ideas and the dissemination of research. These organizations played a crucial role in advancing scientific knowledge and fostering collaboration among researchers.
Charles Darwin’s Evolutionary Theory: A Paradigm Shift

One of the most significant scientific developments of this era was the publication of Charles Darwin’s On the Origin of Species in 1859. Darwin’s theory of natural selection revolutionized biology and had profound implications for religion and society. Key points include:
- Natural Selection: Darwin proposed that species evolve over time through a process of natural selection, where organisms better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. This theory challenged traditional creationist views and sparked intense debate.
- Impact on Religion: Darwin’s work provoked significant controversy, particularly among religious communities. The idea that life could evolve without direct divine intervention challenged established religious doctrines and forced a reevaluation of the relationship between science and faith.
A Period of Dynamic Change
The late 19th and early 20th centuries were a time of dynamic change, where the interplay between technological progress, religious revival, and scientific discovery reshaped society in profound ways. The advancements and debates of this era laid the groundwork for many of the intellectual and cultural developments that continue to influence us today. As we reflect on this period, it’s clear that the convergence of science, religion, and society was not just a backdrop to history—it was a driving force that shaped the modern world.
Crisco and the Industrialization of Food: A Public Health Dilemma

David Wesson’s Innovations: Paving the Way for Processed Fats
Before Crisco became a household name, a critical innovation by chemist David Wesson set the stage for the transformation of cottonseed oil into a viable commercial product. Wesson developed industrial bleaching and deodorizing techniques that removed impurities and odors from cottonseed oil, making it suitable for consumption. These innovations turned what was once considered a waste byproduct of the cotton industry into a popular ingredient in processed foods.

- The Transformation of Cottonseed Oil: Prior to Wesson’s advancements, cottonseed oil was largely discarded due to its unpleasant taste and smell. However, his techniques made it possible to produce a neutral-tasting oil, paving the way for its widespread use in cooking and food manufacturing. This not only provided a new revenue stream for the cotton industry but also introduced a new type of fat into the American diet.
- Setting the Stage for Crisco: Wesson’s innovations in refining cottonseed oil directly influenced the creation of Crisco. In 1911, Procter & Gamble capitalized on this now-viable oil by using it as the base for their new product, Crisco, the first hydrogenated vegetable oil. Crisco was marketed as a cleaner, healthier alternative to traditional animal fats, further embedding processed fats into the American diet.
of nutrition.
The Flexner Report: Redefining Medical Education and Marginalizing Nutrition
The Medicalization of Health
In 1910, Abraham Flexner, an educator commissioned by the Carnegie Foundation, published a report that would fundamentally reshape medical education in the United States. The Flexner Report criticized the state of medical schools at the time, advocating for a more scientific and rigorous approach to medical training. While this led to significant improvements in the quality of medical education, it also had unintended consequences that continue to affect the healthcare system today.
- Pharmaceutical Focus: One of the key outcomes of the Flexner Report was the shift towards a model of medical education that heavily emphasized pharmaceutical treatments and the biomedical approach to disease. This focus on treating symptoms with drugs often sidelined other aspects of health, such as nutrition, lifestyle, and preventive care.
- Marginalization of Nutrition: As medical education became more specialized and disease-focused, the role of nutrition in maintaining health was increasingly neglected. The curriculum in medical schools began to prioritize pharmacology and surgery over dietary interventions and holistic approaches to health. This trend has persisted, contributing to a healthcare system that often overlooks the importance of nutrition in preventing and managing chronic diseases.
- Lasting Impact: The legacy of the Flexner Report is still evident in today’s healthcare system, where physicians receive minimal training in nutrition and preventive care. This has led to a disconnect between the medical profession and the growing body of evidence supporting the role of diet and lifestyle in health. Patients often find that their doctors are more likely to prescribe medication than to offer dietary advice, perpetuating a cycle where symptoms are treated rather than underlying causes.
Rockefeller’s Indirect Role in Crisco’s Creation

One of Rockefeller’s lesser-known ventures was cottonseed oil. Standard Oil was involved in refining oil, and as the company expanded, it ventured into agricultural byproducts like cottonseed oil, which had ties to industrial processes similar to those used in petroleum refining. Rockefeller’s influence in the oil refining industry paved the way for technologies that would later be used in the food industry, such as hydrogenation. Hydrogenation is a process that was originally developed in the oil industry—primarily petroleum.
Crisco and the Industrialization of Food: A Public Health Dilemma
The Rise of Crisco: From Industry to Kitchen
Just a year after the publication of the Flexner Report, Procter & Gamble introduced Crisco, a revolutionary new product that would transform the American diet. Crisco was the first hydrogenated vegetable oil, created through a process that turned cottonseed oil—a byproduct of the cotton industry—into a solid, shelf-stable fat. Marketed as a cleaner, healthier alternative to animal fats like lard and butter, Crisco quickly became a staple in kitchens across the country.

- Industrialization of Food: Crisco’s success marked a significant step in the industrialization of the food supply. It was one of the first mass-produced food products that relied on industrial processes to create something entirely new, rather than simply refining or preserving traditional foods. This innovation paved the way for the widespread use of processed foods, which today dominate the American diet.
- The Introduction of Trans Fats: The hydrogenation process that created Crisco also produced trans fats, which were largely unknown to the public at the time. For decades, trans fats were used extensively in processed foods due to their stability and low cost. However, research eventually revealed that trans fats are highly detrimental to health, significantly increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other chronic conditions.
- Public Health Consequences: The widespread adoption of Crisco and other hydrogenated oils contributed to a dramatic shift in the American diet, away from natural fats and towards processed, industrially produced fats. This shift has been linked to the rise in obesity, cardiovascular disease, and other diet-related health issues that continue to plague the population today.
The intersection of industry, medicine, and nutrition in the early 20th century had profound and lasting impacts on public health. Two significant events—the publication of the Flexner Report in 1910 and the introduction of Crisco in 1911—played pivotal roles in shaping the way we approach food, health, and medicine. These influences continue to resonate in modern healthcare and nutrition science, often to the detriment of public health. Let’s explore how these developments unfolded and the lasting effects they’ve had on our understanding of nutrition.
The Impact of Historical Influences on Nutrition: How the Flexner Report and Crisco Reshaped Public Health
The intersection of industry, medicine, and nutrition in the early 20th century had profound and lasting impacts on public health. Two significant events—the publication of the Flexner Report in 1910 and the introduction of Crisco in 1911—played pivotal roles in shaping the way we approach food, health, and medicine. These influences continue to resonate in modern healthcare and nutrition science, often to the detriment of public health.
The Influence of Religious Movements on Nutrition
Seventh-Day Adventism and Nutritional Reform

The Seventh-Day Adventist Church, founded in the mid-19th century, had a profound impact on American dietary practices. Ellen G. White, a key figure in the church, advocated for dietary restrictions based on her religious beliefs. Her recommendations included vegetarianism, the avoidance of stimulants like caffeine and alcohol, and a focus on holistic health. These recommendations were driven by religious beliefs rather than scientific evidence, leading to misleading dietary practices and a restrictive diet culture rather than genuinely beneficial health habits.

Her health reforms, which emphasized vegetarianism and whole foods, were institutionalized through health institutions like the Battle Creek Sanitarium and figures like Dr. John Harvey Kellogg. The sanitarium’s success and the dissemination of these dietary principles led to the establishment of the American Dietetic Association in 1917, which originally promoted many of these plant-based, whole-food principles. The Adventist emphasis on preventive health care and diet principles laid the groundwork for many modern dietary guidelines and continue to influence discussions around veganism.
Sylvester Graham and the Health Food Movement: A Critical Perspective
Sylvester Graham, a key figure in early American health reform, is often remembered for his influence on the health food movement and the creation of the Graham cracker. However, his dietary principles were deeply intertwined with his moral and religious views, particularly his beliefs about suppressing sexual urges.

The Man Behind the Movement
Sylvester Graham (1794–1851) was a Presbyterian minister whose health reform efforts were driven by more than just a desire for better nutrition. His dietary recommendations were rooted in his belief that physical health was closely linked to moral and spiritual purity. Graham’s ideas were based on the notion that a simpler diet, free from stimulants like caffeine and alcohol, would not only improve physical health but also help suppress sexual desires, which he and his contemporaries saw as a moral failing.
Dietary Principles and Moral Agenda
Graham’s health principles included:
- Vegetarianism: He promoted a diet free from meat, believing it would enhance both physical health and moral restraint.
- Avoidance of Stimulants: He advised against consuming caffeine and alcohol, which he associated with negative moral and physical effects.
- Simplicity and Moderation: His diet emphasized plain, unprocessed foods and self-restraint.
Graham’s dietary reforms were part of a broader attempt to control what he saw as unhealthy and immoral behavior. He believed that a disciplined diet would help curb sexual urges, which he viewed as a major threat to individual and societal purity.
The Graham Cracker: A Tool for Reform
The Graham cracker, a product of Graham’s dietary reform, was created with the intention of supporting digestive health and satisfying cravings in a morally acceptable way. While it has become a popular snack, its creation was driven by Graham’s broader health and moral agenda. The cracker was designed to be a healthful alternative to more stimulating and indulgent foods.
Graham’s dietary principles were part of a larger movement that sought to reform not just food habits but also moral behavior. His ideas reflected a concern with maintaining moral purity through dietary control, a concept that influenced various health reform efforts of the time. However, it’s important to recognize that many of Graham’s claims were not based on rigorous scientific evidence but rather on his own beliefs and the prevailing moral attitudes of his era.
While Graham’s advocacy for dietary reform contributed to the development of health foods and the broader health movement, his ideas were also deeply entwined with his attempts to control sexual behavior. This connection reflects a historical context where dietary practices were often used as a means of enforcing moral and social norms.
The Graham cracker, though still a common snack, serves as a reminder of the complex interplay between health reform and moral ideologies. Today, it’s essential to approach such historical figures with a critical understanding of how their personal beliefs influenced their recommendations.
Sylvester Graham’s impact on the health food movement was significant, but it was also rooted in a broader moral agenda that sought to suppress sexual urges through dietary control. While his ideas helped shape dietary practices and health food development, they were not always grounded in scientific evidence. By understanding the historical context of Graham’s work, we can better appreciate the evolution of dietary reform and the need for evidence-based approaches to health.
Learning from History: Integrating Nutrition into Modern Health Practices
The historical narratives of the Flexner Report, Crisco, and influential dietary movements like Seventh-Day Adventism reveal the intricate connections between industry, religion, and health. The Flexner Report’s emphasis on pharmaceuticals and Crisco’s promotion of processed fats underscores significant shifts in health practices that have had lasting impacts on public health.
A Shift in Priorities: The Flexner Report’s focus on pharmaceuticals often came at the expense of a more holistic understanding of health, one that includes nutrition and lifestyle as key components. Similarly, the industrialization of food, exemplified by Crisco, introduced dietary patterns that are now recognized as harmful.
Learning from History: As we continue to navigate challenges in nutrition and healthcare, it’s crucial to reintegrate a holistic approach to health that includes both nutrition and preventive care. Recognizing the historical impacts of these developments helps us advocate for a healthcare system that values comprehensive care and a food industry that prioritizes public health over profit.
Reclaiming Health Through Nutrition
Ellen G. White’s health reforms, emphasizing vegetarianism and whole foods, were institutionalized by the Battle Creek Sanitarium and figures like Dr. John Harvey Kellogg. This led to the 1917 founding of the American Dietetic Association, initially promoting these principles. Meanwhile, the Flexner Report and Crisco’s introduction highlight historical forces shaping health and nutrition. These events underscore the need for a holistic health approach that integrates nutrition and addresses industrialization’s impacts. Moving forward, it’s crucial to advocate for a healthcare system focused on preventive care and a food industry that prioritizes public health.
As we wrap up our exploration of conspiracy chronicles this week, we’ve uncovered how the 20th century marked a pivotal shift in the rise of political paranoia and corporate influence. Powerful corporations, fueled by rapid technological and social changes during the Second Industrial Revolution, began to wield unprecedented control. From the Fletcher Report to the invention of Crisco and Ancel Keys’ flawed dietary research, lobbying and payoffs set the stage for policies that still impact public health today.
In fact, a 2020 study revealed that 95% of members on the Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee have conflicts of interest with industry giants like Kellogg, General Mills, Kraft, and Dannon. These ties, whether through research funding or board memberships, call into question the impartiality of public health recommendations. With corporate agendas deeply embedded in sectors like food and pharmaceuticals, the guidelines shaping what we eat are under scrutiny, reminding us that the influence of these forces remains a pressing issue. Read more here.
📚 Further Reading
Dive deeper into these captivating topics with these resources:
- The Rise and Fall of Crisco: An exploration of Crisco’s impact on the American diet.
- The Forgotten Saga of Crisco: A look at the historical significance of Crisco in American food culture.
- How Crisco Made Americans Believers in Industrial Food: Examining Crisco’s role in transforming American dietary habits.
Explore these intriguing developments and see how they continue to shape our understanding of health, religion, and science today. 🌟
If you’re looking to explore the topic of conflicts of interest in the U.S. food system, including the influence of corporate lobbying on dietary guidelines and public health, here are some credible resources:
- Marion Nestle’s Work
Marion Nestle, a renowned nutritionist and public health advocate, has extensively written about the politics of food and how corporate interests shape food policies. Her book “Food Politics: How the Food Industry Influences Nutrition and Health” is a foundational resource that explores conflicts of interest in detail. She has also published several articles and blog posts that can be found on her website, Food Politics. - The Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI)
CSPI is a non-profit organization that advocates for public health and transparency in the food industry. They regularly publish reports and articles on how industry lobbyists influence dietary guidelines and public health policies. Visit their site for comprehensive resources: CSPI. - The Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA)
JAMA has published several peer-reviewed articles on the conflicts of interest within the committees that develop dietary guidelines. You can access these studies through JAMA. - The Union of Concerned Scientists (UCS)
UCS focuses on the intersection of science, policy, and industry influence, and they have published reports on the food industry’s role in shaping guidelines. You can find their reports here: UCS Food System Work. - Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s Health Freedom Platform
RFK Jr.’s organization, Children’s Health Defense, provides reports and articles on corporate influence in healthcare and the food system. While this source may reflect RFK Jr.’s specific views, it offers insights into his arguments and data regarding industry control. Children’s Health Defense.
🏷️ Tags
#saturatedfat #nutrition #podcast #fitness #conspiracies #nutritionhistory #historylesson #funfacts