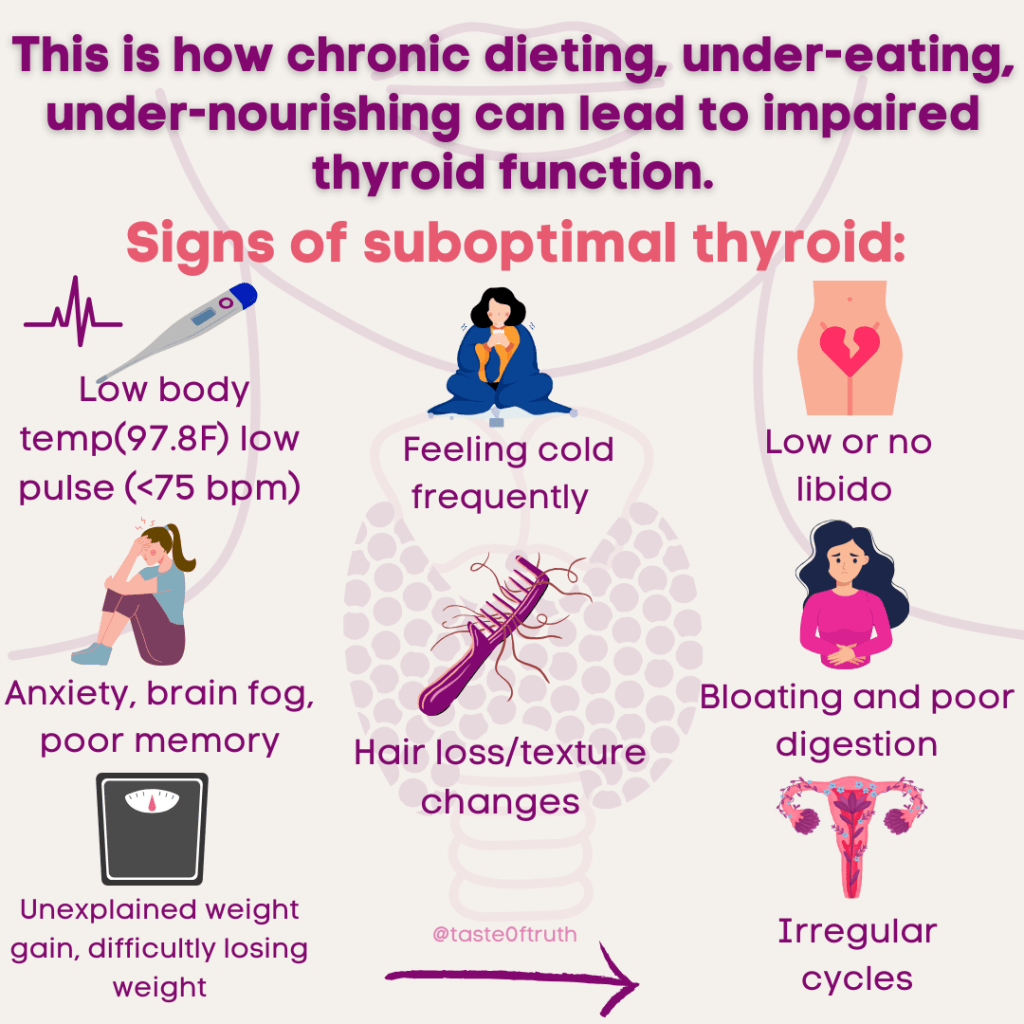
The Fatal Flaws of Calories In Calories Out and the Metabolism Model That Could Change Everything
Alright, let’s talk about the four most useless words in the history of weight loss advice: ‘Just eat less, move more.’ You’ve heard it, I’ve heard it, and if this phrase actually worked the way people think it does, we wouldn’t have skyrocketing rates of obesity, metabolic dysfunction, and entire industries built around yo-yo dieting. But here’s the kicker—it sounds logical. Simple math, right? Calories in, calories out. Except the human body is not a bank account; it’s a biological orchestra, and the way we process energy is more like a symphony than a spreadsheet.
We’ve already tackled the oversimplified calorie-counting dogma in our Science Dogma episode, and we’ve explored how perception alone—like believing a milkshake is ‘indulgent’—can literally alter our hormonal response. That’s not woo-woo, that’s science. But today, we’re going deeper. Because beyond the CICO model, beyond the calorie obsession, there’s a much bigger, messier, and more fascinating reality about metabolism, obesity, and why diet advice keeps failing people.
And I know what some of you might be thinking—‘But Megan, are you saying calories don’t matter?’ No. I’m saying they don’t tell the whole story. The way we eat, when we eat, why we eat, our hormones, stress levels, metabolic adaptations, even our past dieting history—all of it plays into how our body responds to food.
So as we close out Season 3 of Taste of Truth Tuesday, I want to leave you with something foundational. Not another diet trend. Not another oversimplified soundbite. But a real, nuanced conversation about what actually influences metabolism, weight loss, and why some of the most popular strategies—like keto, intermittent fasting, and calorie counting—work for some people but absolutely wreck others.
And here’s the disclaimer—I’m not an advocate for low-carb dieting in general, especially as someone who’s recovered from disordered eating. But my guest today? He eats low-carb and keto. And here’s what I respect—he’s not dogmatic about it. He understands that the real answer to health and weight loss isn’t found in any one-size-fits-all approach. It’s about bio-individuality.
So grab your coffee, take a deep breath, and get ready to rethink everything you thought you knew about metabolism. Let’s do this.
The calorie, as a unit of measurement, has a fascinating history that ties directly into the calories in, calories out (CICO) debate. While many assume the calorie has always been the standard for measuring food energy, its adoption in nutrition is relatively recent and shaped by shifts in scientific understanding, industry influence, and public health narratives.

The Origin of the Calorie
The concept of the calorie originated in physics, not nutrition. In the early 19th century, Nicolas Clément, a French chemist, introduced the term calorie as a measure of heat energy. By the late 1800s, scientists like Wilbur Olin Atwater adapted this concept to human metabolism, conducting bomb calorimeter experiments to determine how much energy food provided when burned. Atwater’s Physiological Fuel Values established the foundation for modern caloric values assigned to macronutrients (fat = 9 kcal/g, carbohydrates and protein = 4 kcal/g, alcohol = 7 kcal/g).

The Rise of Caloric Nutrition
By the early 20th century, calories became central to dietary guidelines, especially in public health efforts to address malnutrition. During both World Wars, governments used calorie counts to ration food efficiently. However, as food abundance grew, the focus shifted from ensuring sufficient calorie intake to preventing excess, paving the way for weight-focused dietary interventions.
CICO and the Simplification of Weight Loss
The calories in, calories out model became dominant in the mid-20th century, driven by research showing that weight loss or gain depended on energy balance. The First Law of Thermodynamics—energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed—was applied to human metabolism, reinforcing the idea that a calorie surplus leads to weight gain and a deficit to weight loss.
This framework became the foundation of mainstream diet advice, but it often overlooked complexities such as:
- Hormonal influences (e.g., insulin, leptin, ghrelin)
- Metabolic adaptation (how bodies adjust to calorie deficits)
- The thermic effect of food (protein takes more energy to digest than fat or carbs)
- Gut microbiome effects on calorie absorption
- Psychological and behavioral aspects of eating
Criticism and the Evolution of the Debate
By the late 20th century, challenges to strict CICO thinking emerged. Researchers in endocrinology and metabolism, such as Dr. Robert Lustig and Dr. David Ludwig, highlighted that not all calories affect the body in the same way—insulin regulation, macronutrient composition, and food quality play crucial roles.
Low-carb and ketogenic diet advocates argued that carbohydrate restriction, not just calorie restriction, was key to weight management due to its impact on insulin and fat storage.
I personally think, it’s not just carbs or calories doing this. There are at least 42 factors that impact blood sugar and metabolism. This is something I’ve worked to educate my audience on for years. Carbs are just one piece of the puzzle. Stress, sleep, gut microbiome, meal timing, inflammation, hormonal balance—all of these influence the body’s metabolic “terrain.”
Where Are We Now?
Today, the calorie remains a useful measure, but the conversation has expanded beyond simple energy balance. Researchers acknowledge that while calories matter, factors like food quality, hormonal responses, and individual metabolic differences significantly impact how the body processes energy. The debate now leans toward a more nuanced view.
Now, let’s talk about why this matters.
Today, I’m joined by Adam Kosloff, an author and researcher who isn’t afraid to challenge conventional wisdom—especially when it comes to obesity and metabolism. A Substack post of his, A Righteous Assault on the Absolute Worst Idea in the History of Science, takes a sledgehammer to the dominant ‘calories in, calories out’ model, aka Move More, Eat Less? The Lie That Won’t Die, arguing that our understanding of fat storage is fundamentally broken. Instead, he presents a revolutionary new framework—the Farmer Model—that redefines how we think about metabolism, obesity, and weight loss.
For years, the dominant narrative around weight loss has been depressingly simple: “move more, eat less.” This slogan has been drilled into us by dietitians, doctors, and fitness gurus as if it were an unshakable law of physics. But if it were that simple, why has metabolic disease skyrocketed despite more people tracking their calories and increasing exercise?
Adam challenges the traditional CICO (calories in, calories out) model, not just by saying it’s wrong, but by arguing it is catastrophically misleading. His Farmer Model reframes obesity and metabolic dysfunction as a landscape issue rather than a simple calorie balance equation.
Think of your metabolism like farmland. The most obvious disruptor might be “acid rain”—high-carb, sweet, ultra-processed foods that erode the topsoil, flood the land, and cause metabolic damage (fat storage, inflammation, insulin spikes). But not all disruptions look like a storm.
Sometimes, the changes are more insidious. Maybe those daily lattes weren’t a flood but a subtle shift in the terrain, like over-fertilizing a field. Too much of a good thing, whether dairy proteins or artificial sweeteners, can nudge the metabolic landscape in a way that leads to dysfunction over time.
And here’s the kicker: It’s not just carbs or calories doing this. There are at least 42 factors that impact blood sugar and metabolism. This is something I’ve worked to educate my audience on for years. Carbs are just one piece of the puzzle. Stress, sleep, gut microbiome, meal timing, inflammation, hormonal balance—all of these influence the body’s metabolic “terrain.”
Adam’s latest Substack post, 10 Smackdowns That Lay Waste to CICO, was an absolute banger. The line “Gaze upon these arguments, ye mighty gym bros, and despair…” had me cackling. But beyond the sass, the research was rock solid. In our conversation, we break down some of the most devastating smackdowns against CICO and discuss which ones tend to make the most die-hard calorie counters short-circuit.
The takeaway? The “move more, eat less” doctrine is outdated and incomplete. It’s time for a more sophisticated conversation about metabolism that acknowledges the complexity of the human body rather than reducing it to a basic math equation.
LINKS
Science or Stagnation? The Risk of Unquestioned Paradigms – The first episode we challenged calories in, calories out (CICO) & mention Germ theory vs Terrain theory
10 Smackdowns that lay waste to CICO
3 Times I Gained Weight on Keto
Emotional Hijacks & Nutritional Hacks: Unveiling the🧠Amygdala’s Secrets
The Dissolution of the Nutrition Science Initiative
Obesity and Starvation Found Together
The Influence of Religious Movements on Nutrition
Why Challenging Beliefs Feels Like a Personal Attack—And Why It Shouldn’t