How to Use Temperature and Pulse for Metabolic Health Insights
In the summer of 2020, my health began to take a dive. Years of chronic dieting, over-exercising, negative self-talk, and hormonal birth control were taking their toll. I was eating next to no carbs, minimal sugar, low fat, no dairy, and only lean protein. I was working out six days a week, doing hours of cardio, and feeling terrible physically, mentally, and emotionally. Hypothyroid and adrenal symptoms began to emerge. It was clear my lifestyle was working against my physiology. My metabolism felt ‘broken’ or ‘slow,’ but in reality, I was undernourished and overstressed.
Initially, I started tracking basal temperature but did not include resting pulse rates. At the time, my average temperatures were 96.5°F, and my pulse was 44 bpm. Discovering the “pro-metabolic” community introduced me to the research of Dr. Ray Peat and Dr. Broda Barnes, and it changed my perspective.
According to Dr. Raymond Peat, a well-nourished, healthy human should have a resting pulse of 85+ beats per minute. A high resting pulse (in the absence of stress) indicates good metabolic health and a strong ability to repair. This counters mainstream advice, which often celebrates a low resting heart rate as a marker of fitness.
Why Temps and Pulses Matter
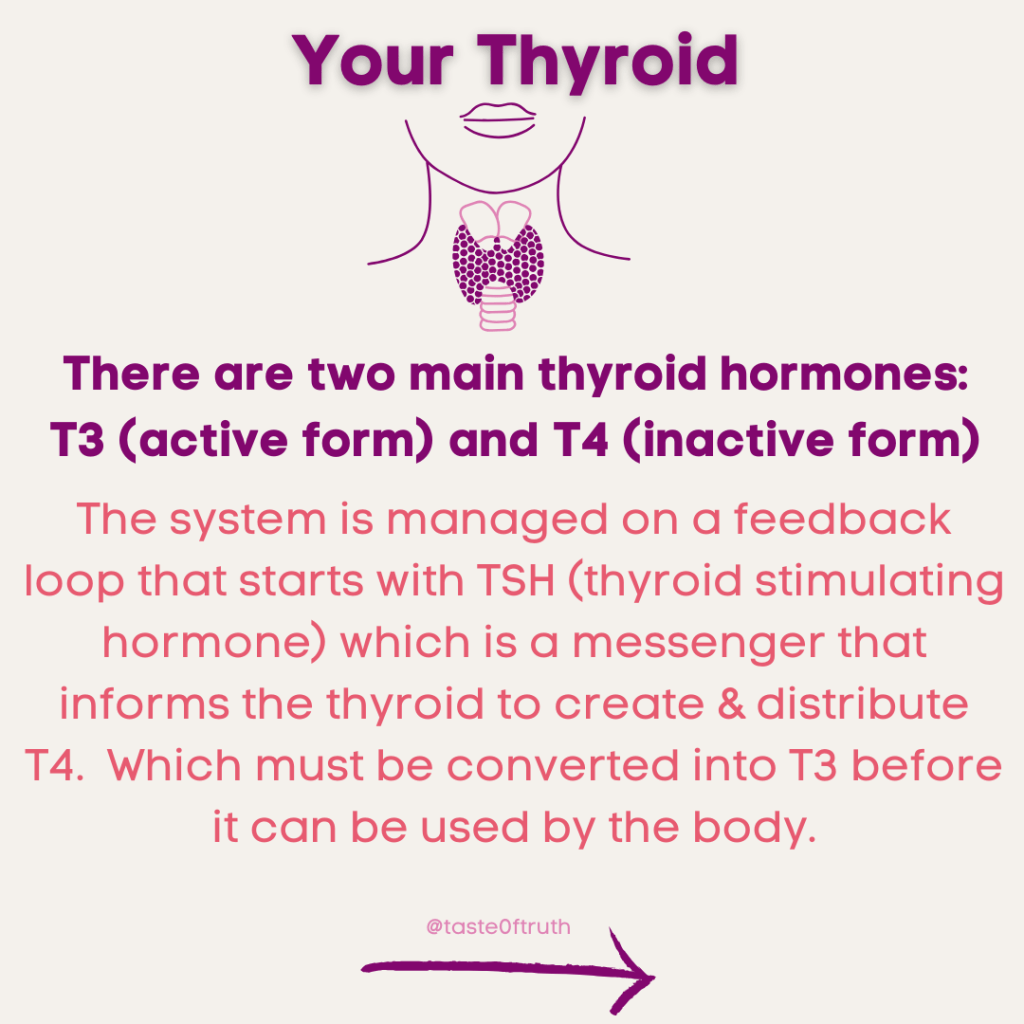
Your thyroid acts as your body’s thermostat, controlling metabolism. Metabolism is the sum of all biochemical reactions in the body—essentially, the rate of energy production in the cells and the speed of bodily processes. Body temperature reflects metabolic activity, and people with underperforming thyroids often have low basal body temperatures.
Tracking basal body temperature and resting pulse provides insights into your thyroid and metabolic function:
- Basal body temperature can indicate if ovulation has occurred, reflecting progesterone production (a pro-thyroid hormone).
- Resting pulse shows how well your body is utilizing nutrients and oxygen.
- Tracking post-meal temperatures and pulses helps identify stress responses and metabolic efficiency.
How to Track Temps and Pulses
To get accurate and actionable insights, follow these steps: Log your readings daily to identify trends over time. Note factors like stress, sleep, meals, and menstrual cycle phases that might influence your results.
- Choose the Right Thermometer
- Use a digital thermometer with a quick response time and high accuracy.
- Glass basal thermometers are also effective but require more time to measure.
- Measuring Basal Temperature
- Take your temperature first thing in the morning, immediately after waking, and before getting out of bed.
- Place the thermometer under your tongue for the most reliable reading. Avoid using armpit readings as they can be less accurate due to environmental factors.
- Measuring Resting Pulse
- Use a wearable device, like a fitness tracker, to measure your resting pulse overnight or immediately upon waking.
- Alternatively, place your index and middle fingers on your wrist or neck to manually count beats for 60 seconds.
- After Meals
- Check your temperature and pulse 30-40 minutes after breakfast. These should gently rise after eating, as food lowers stress and generates heat. If they drop, it may indicate elevated stress hormones upon waking.
- Track Afternoon Readings
- Record your temperature and pulse between 1-3 p.m. when your body’s temperature should naturally peak.
- Use a Tracking App or Journal
Questioning the Mainstream Narrative
The Mayo Clinic states: “Generally, a lower heart rate at rest implies more efficient heart function and better cardiovascular fitness. For example, a well-trained athlete might have a normal resting heart rate closer to 40 beats per minute.”
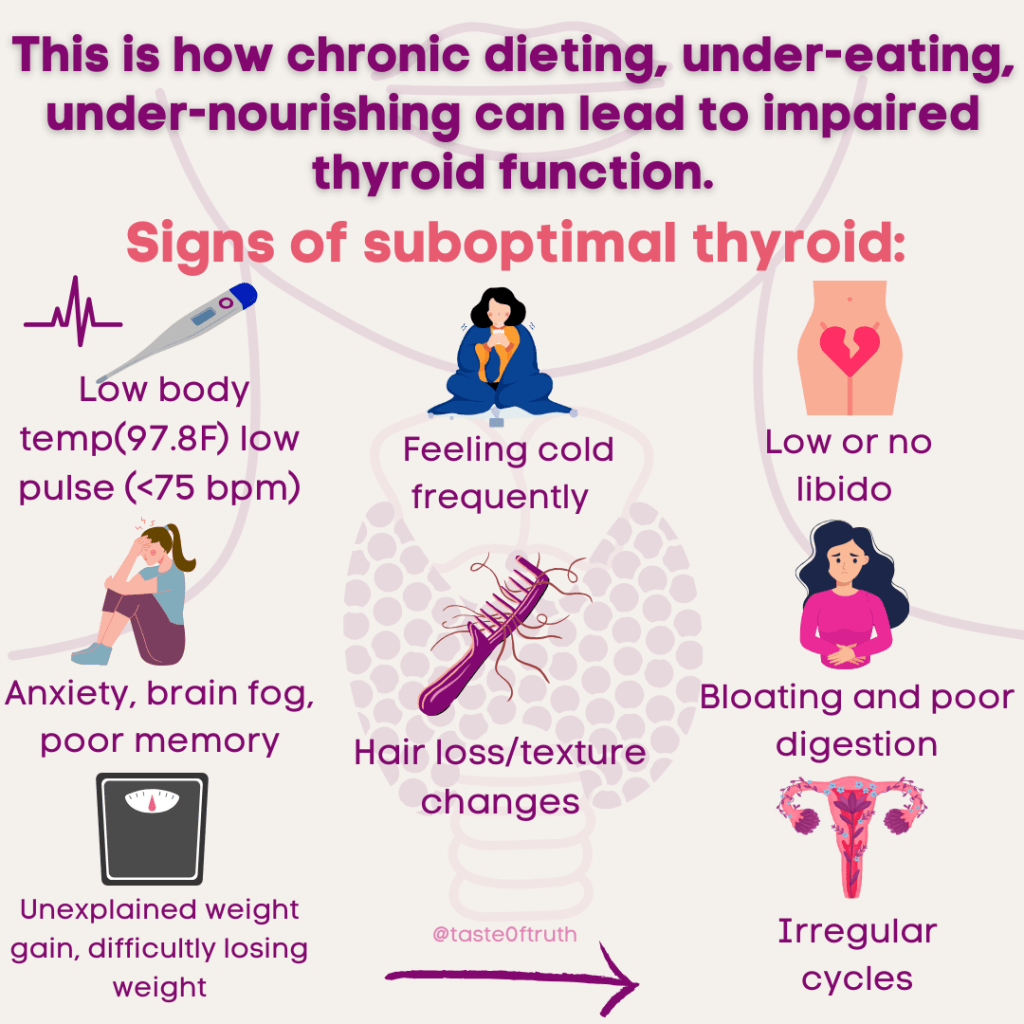
But is a low resting heart rate truly beneficial? Evidence suggests otherwise. Thyroid health—the thermostat of the body—plays a crucial role in metabolism. A sluggish thyroid often correlates with lower body temperatures and slower heart rates, indicators of reduced metabolic function.
Why Temperature and Pulse Matter

Metabolism refers to the sum of all biochemical reactions in the body. It’s essentially the rate of energy production at the cellular level—the speed at which your body processes and utilizes energy. Your body temperature is a reflection of this activity. People with under-functioning thyroids tend to exhibit low basal body temperatures and slower pulses, which can indicate:
- Low thyroid function
- Inflammation
- Suppressed immune function
- High stress
- Estrogen dominance
In contrast, a warm body is linked to better immune function, efficient digestion, reduced inflammation, and overall metabolic health.

How to Track Temperature and Pulse
Tracking these metrics throughout the day provides invaluable insights into your metabolic health:
- Upon Waking:
- Follicular Phase: 97.2-97.8°F
- Luteal Phase: 98.6°F
- Resting pulse: 75-90 bpm
- After Breakfast:
- Temperatures and pulse should gently rise after meals. Food lowers stress and generates heat. If your numbers drop, it may indicate falsely elevated waking temps due to stress hormones like cortisol.
- Afternoon:
- Temperatures should peak between 1-3 PM.
What Your Numbers Reveal
- Higher temp and pulse (in the absence of stress): Optimal metabolic function
- Normal temp and higher pulse: Active stress response
- Lower temp and lower pulse: Chronic stress and metabolic suppression
- Normal temp and lower pulse: Chronic stress or low thyroid function
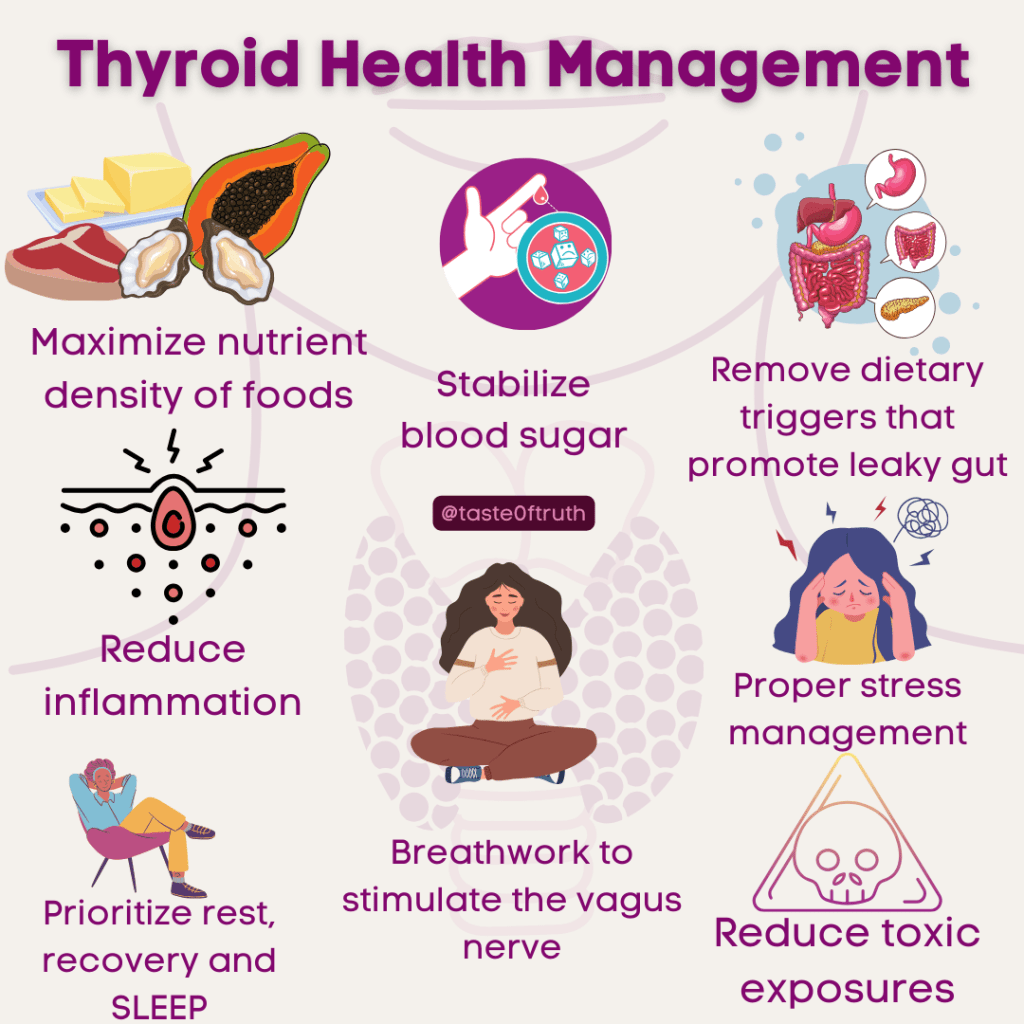
How to Optimize Your Numbers
If your temperature and pulse rates aren’t within optimal ranges, consider the following steps:
- Prioritize bioavailable protein: Aim for at least 100 grams per day.
- Eat enough calories: 1,800-2,000+ per day, depending on individual needs.
- Include digestible carbs: At least 150 grams daily (e.g., honey, maple syrup, fruit, root vegetables).
- Pair carbs with protein: Avoid “naked carbs” to stabilize blood sugar.
- Focus on anabolic exercise: Build muscle with strength training to boost metabolism.
Why This Matters
Using temperature and pulse as tools, you can:
- Monitor how well your body utilizes energy.
- Evaluate recovery from exercise.
- Gain insights into hormonal balance (e.g., progesterone production and ovulation).
- Identify the impacts of stress on your physiology.
Final Thoughts
Key Takeaways By regularly monitoring your temps and pulses, you can uncover patterns and make adjustments to optimize your thyroid and metabolic health. These small, daily practices provide powerful insights into how your body is functioning and what it needs to thrive.
Healing is never a final destination; it’s an ongoing journey. Over time, I’ve seen significant improvements in my metabolic markers. My overall body temperature has risen to 97.6–98.1°F, and my resting pulse is now around 70 bpm—much better than where I started. This progress has required me to embrace a larger body size than what traditional “fit fam” culture promotes, but it has been worth it. Prioritizing healing and hormone rebalancing has provided my body with the sense of safety and stability it needed to thrive.
To read more about the doctor that pioneered these tests grab the book called Hypothyroidism: The unsuspected illness by Dr. Broda Barnes
✌🏼Looking for more support navigating your cycle with fitness & nutrition? Check out my FREE guide & pro-metabolic strength training guide available for purchase!
LINK to apply for 1:1 coaching ❤️
Sources 👇🏻
PMID: 28740582
PMID: 26792255
Dr. Ray Peat