When clients come to me saying they have a “slow metabolism” or a “broken” metabolism, often they think they need to eat even less or cut carbs to jumpstart weight loss. But let me flip the script: in many cases, it’s actually chronic under-eating and restrictive dieting that’s slowing down their metabolism. Chronic dieting, especially with very low calories, can lead to impaired thyroid function and ultimately disrupt how the body uses energy. Here’s how it happens and what you can do to restore balance.
What is the Thyroid and Why Does It Matter?
Your thyroid is a small gland in your neck that plays a massive role in regulating your body’s metabolism. Often called the “controller” of metabolic function, the thyroid works closely with the hypothalamus and pituitary glands in the brain to maintain your metabolic rate. This system allows your body to increase or decrease energy production based on its needs, influencing everything from how you process food to your body temperature.
The thyroid primarily produces two hormones:
- T3 (Triiodothyronine) – the active hormone that your cells use.
- T4 (Thyroxine) – the inactive hormone that must be converted into T3 before your body can use it.
The production and conversion of these hormones depend on a feedback loop that begins with TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone), which signals the thyroid to produce and release T4. But when the body is stressed—especially due to chronic under-eating or extreme calorie restriction—this whole process can become disrupted.
How Chronic Dieting Wrecks Your Thyroid
Under-eating is a significant source of stress for the body. Dieting or calorie restriction triggers the HPA axis (Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal axis), leading to an increase in CRH (Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone) and cortisol, our primary stress hormone. High cortisol levels can interfere with thyroid function in the following ways:
- Reduces TSH Production: Elevated cortisol inhibits TSH, lowering T4 production and decreasing the amount of thyroid hormone available for energy use.
- Impairs T4-to-T3 Conversion: Chronic stress slows down the conversion of T4 (inactive) into T3 (active), reducing your body’s energy production.
- Increases rT3 Levels: Instead of converting into T3, some T4 becomes reverse T3 (rT3), a hormone that blocks T3 from being used. This, in turn, reduces the sensitivity of your cells to thyroid hormones, further lowering metabolic function.
This is why individuals who chronically under-eat or yo-yo diet often experience symptoms of hypothyroidism, even without an official diagnosis.
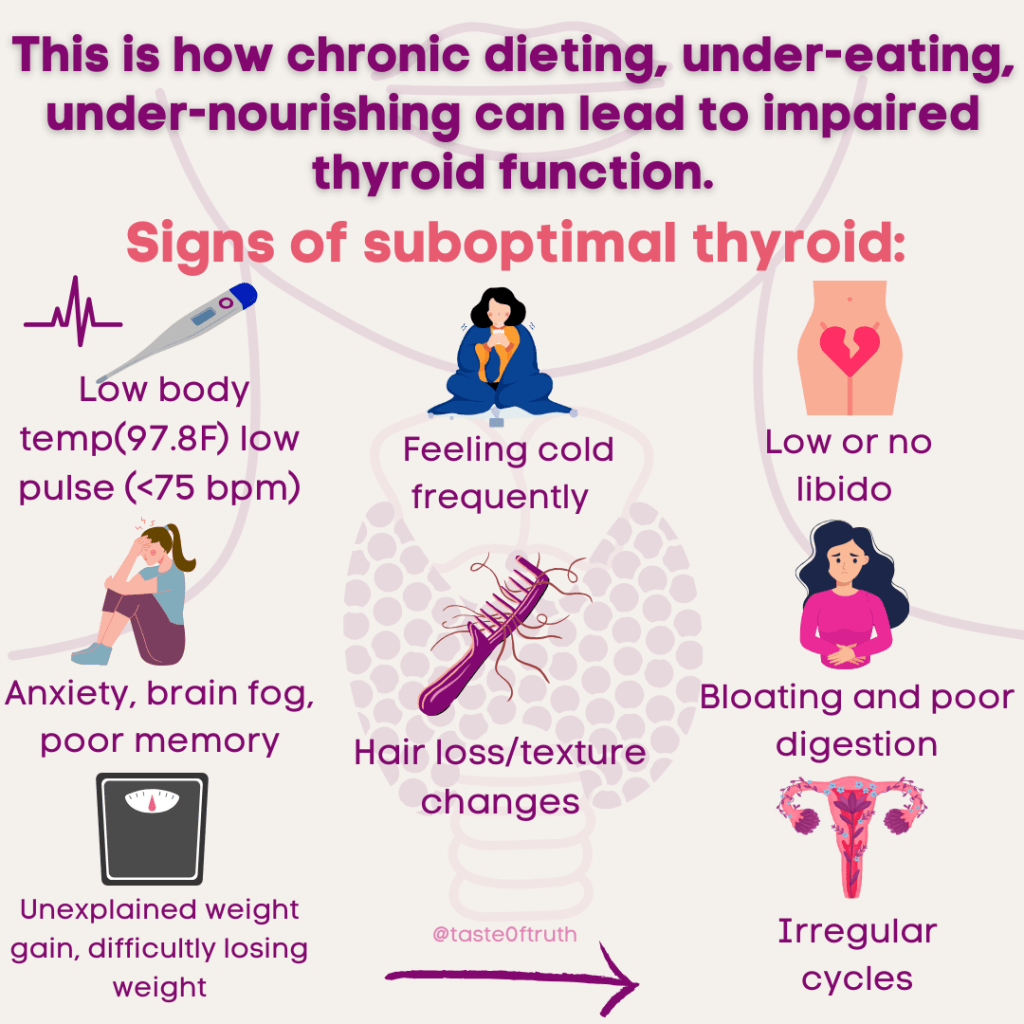
Symptoms of Suboptimal Thyroid Function
If your thyroid isn’t functioning optimally, you may notice some of the following symptoms:
- Low body temperature (below 97.8°F)
- Frequent feelings of cold, regardless of weather
- Low or no libido
- Anxiety, brain fog, or poor memory
- Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Bloating, poor digestion
- Changes in hair texture or hair loss
Many clients experiencing these symptoms have been stuck in a calorie-deficit mindset for years, keeping their bodies in a constant state of stress. As a result, they’re often dealing with adrenal dysfunction, hypothyroidism, or even reproductive health issues, like extreme PMS, cycle loss, or low testosterone.

Restoring Your Thyroid Health—The First Steps
To begin improving thyroid health, our initial goal is to support both psychological and physiological balance, moving away from restrictive dieting and focusing on nourishment. Here’s a breakdown of the steps:
- Stabilize Blood Sugar: Balanced blood sugar supports thyroid health and reduces stress on the body.
- Maximize Nutrient Density: Prioritize whole, nutrient-rich foods to ensure your body receives adequate vitamins and minerals, especially selenium, zinc, and iodine, which are crucial for thyroid function.
- Reduce Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can further stress the thyroid. Anti-inflammatory foods and lifestyle practices can help.
- Incorporate Breathwork: Simple breathwork techniques can stimulate the vagus nerve, helping to regulate the HPA axis and reduce stress.
- Avoid Dietary Triggers: Reduce foods that promote “leaky gut,” such as highly processed foods, sugar, and gluten, if sensitive. This protects your immune and thyroid health.
- Manage Stress Proactively: Yoga, meditation, journaling, or spending time in nature can help keep cortisol in check.
- Reduce Toxins and Pollutants: Environmental toxins can interfere with hormone health, so minimizing exposure can be a powerful step.
- Prioritize Rest and Sleep: Quality sleep allows the body to recover and reset, which is essential for thyroid health.
The Bottom Line
Restrictive dieting isn’t the solution to a slow metabolism; it’s often the root cause. Chronic under-eating can lead to imbalances in your thyroid and adrenal glands, ultimately slowing down your metabolic rate and making it harder to achieve your fitness goals. Rebuilding a balanced, nourished body will not only help you feel better but will also lay the foundation for sustainable health.
This week, we’re talking all things thyroid health, and this post breaks down why breaking free from the dietary dogma of diet culture is crucial! Ever feel like your energy’s tanked, your minds in a fog, or your metabolism’s stuck in slow motion? 🧠✨ You’re not alone, and it could be your thyroid talking.
On this week’s Taste of Truth Tuesdays, we’re joined by Nicole, a holistic health advocate who’s here to shed light on how diet culture’s obsession with restriction can wreak havoc on your thyroid. From her own experience facing an autoimmune diagnosis to her advocacy for individualized nutrition, Nicole breaks down how restrictive dieting not only slows your metabolism but also impacts hormone balance, brain clarity, and overall well-being. Join us to learn how making friends with food (yes, even carbs!) might be the best way to support your thyroid and reclaim your energy.

