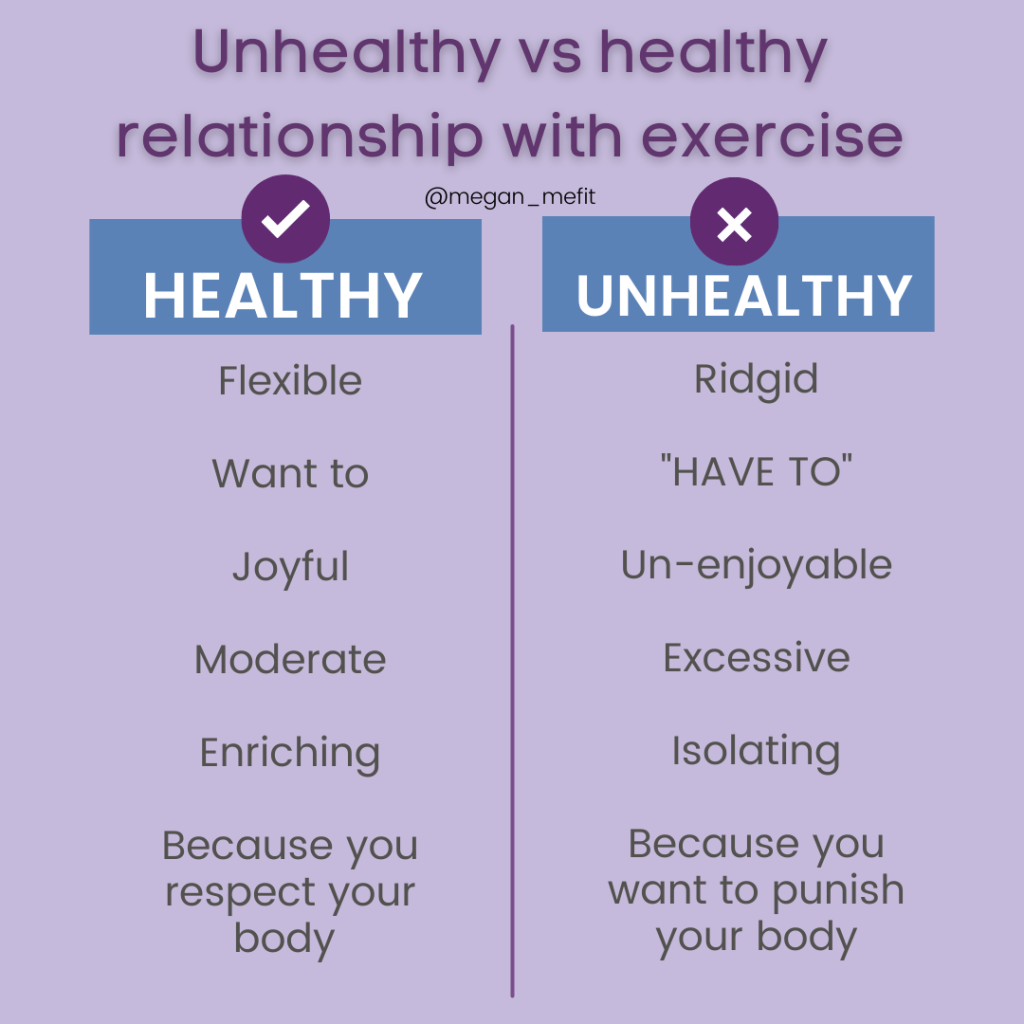
Over the past year, we’ve explored a web of interconnected topics—religious extremism, theology, the role of social media in radicalization, and most recently, body image and the impact of fitspiration.
These discussions aren’t isolated; they all trace back to a common thread—how external influences shape our beliefs, behaviors, and sense of identity. Today, we’re diving deeper into that connection, looking at how beauty standards, social media, and the normalization of self-objectification are part of a larger cultural shift.
The Evolution of Body Image: From Calorie Counting to the Cult of Fitness
Our cultural obsession with body modification isn’t new—it’s just evolved.
In The Body Project, historian Joan Jacobs Brumberg explores the history of American girls and how today women have more freedom and choice than ever before, but many of us begin a pattern of negative self-image, beauty obsession and dieting as early as five or six. Brumberg states:
“All throughout history, adolescent self-consciousness is quite persistent, but it’s level is raised or lowered, like the water level in a pool, by the cultural and social setting.”
For instance, in the late 19th century, girls might have been particularly conscious of their hands and feet due to the fashion and modesty standards of the time, as well as the emphasis on delicate and proper presentation. Additionally, the ideal feminine silhouette of the time, with tightly laced corsets and voluminous skirts, might have made girls more conscious of their waists and overall body shape.
So, while in modern day times, we may cringe at the confinements of what the Victorian society and wearing the corset did to women, but I’d like to argue that in 2025 body angst is driven by much more sinister forces. Today, commercial interests utilize marketing strategies that result in enormous amounts of profit for the manufactures of cosmetic, surgery, hair products and of course diet foods.
The reality that American girls now center their lives around their bodies is neither coincidental nor trivial: it reflects historical shifts that are just now being comprehended.

Brumberg examines how the modern fixation on weight began in the early 20th century. Historically, the surge of explicit “girl talk” about body and sexuality is a relatively recent American phenomenon. As the language surrounding sex and the body has evolved, so too have the body projects of different generations of American girls. By the 1920s, girls began writing about their efforts to develop sexual allure through clothing and cosmetics, and for the first time, they experimented with “slimming”—a new body project tied to the scientific discovery of the calorie. The dieters and sexual players of the 1920s were generally girls in middle to late adolescence, finishing high school or heading off to college and jobs in the business world—unlike today, where such concerns often affect younger children and teenagers.
By the 1970s and 1980s, body control became about more than just being thin; it evolved into sculpting the ideal physique. This shift gave rise to what we now recognize as the cult of fitness—a movement that reframed body control as discipline and self-mastery. The rise of bodybuilding, aerobics, and the emerging diet industry all played a role in selling the idea that, with enough effort, anyone could build their “dream body.”

The Role of Genetics in Muscle Growth: What Fitness Culture Gets Wrong
But science tells a different story. While training and nutrition matter, genetics play a massive role in muscle development, strength, and even fat distribution. A study published in Communications Biology (2020) found that an individual’s ability to build muscle and strength is 50-80% genetic (Pei et al., 2020).
This means that two people following the exact same training program and nutrition plan will not achieve the same results—because their genetic blueprint largely determines their potential for muscle growth, recovery speed, tendon strength, and even motivation to train.
Yet, fitness culture—including myself as a personal trainer for nearly 20 years—rarely acknowledges this, pushing the narrative that extreme discipline alone is the key to achieving a certain look. This myth is not only misleading but also damaging, leading many people to believe that if they just worked harder, ate “cleaner,” or followed the right influencer’s workout, they could look like a fitness model.
How Genetics Impact Strength and Muscle Development
- Muscle Fiber Composition: The Fast-Twitch vs. Slow-Twitch Factor
- People with a higher percentage of fast-twitch muscle fibers (Type II) have a genetic advantage in strength and hypertrophy (muscle growth). These fibers respond better to resistance training and grow larger than slow-twitch (Type I) fibers, which are more endurance-focused.
- Some individuals are naturally fast-twitch dominant, making it easier for them to build muscle. Others are slow-twitch dominant, meaning they may struggle with size gains but excel in endurance sports like long-distance running (Timmons et al., 2010).
- Myostatin: The Genetic “Muscle Growth Brake”
- Myostatin is a protein that regulates muscle growth by preventing muscles from getting too large.
- People with lower levels of myostatin (due to genetic mutations) have an easier time building muscle naturally. Some bodybuilders and elite athletes are born with myostatin deficiencies, giving them an unfair advantage (Lee & McPherron, 2001).
- Testosterone and Hormonal Variability
- Testosterone is a major driver of muscle protein synthesis, and its levels vary wildly among individuals.
- Some people naturally produce more free testosterone (the biologically active form), which enhances muscle recovery, strength, and hypertrophy.
- Women generally have 10-20 times lower testosterone levels than men, making significant muscle gains much harder without pharmacological assistance (i.e., steroids) (Kraemer et al., 1998).
- Bone Structure and Muscle Insertions: The Aesthetic Factor
- Ever wonder why some people seem to have a “naturally sculpted” look even before they start training?
- Bone structure (such as clavicle length, rib cage width, and hip-to-waist ratio) dictates how muscle mass is distributed.
- Muscle insertion points vary genetically, meaning some people have longer muscle bellies, which create fuller-looking muscles, while others have shorter insertions, making certain muscles appear smaller or less defined no matter how much they train (Abe et al., 2016).
The Dangerous Myth of “Hard Work = Guaranteed Results”
Fitness influencers, personal trainers, and the entire “no excuses” culture have sold the idea that discipline alone determines success. And yes—training consistency and proper nutrition absolutely matter. But they will never override genetic limitations.
This myth leads to:
- Unrealistic Expectations: People blame themselves when they don’t achieve Instagram-worthy physiques, despite training and eating “perfectly.”
- Overtraining & Injury: Chasing unrealistic body standards leads many to overtrain, ignore recovery, and develop chronic injuries.
- Disordered Eating & Supplement Abuse: Some resort to extreme dieting, excessive protein intake, or even performance-enhancing drugs to push past genetic limits.
The Industry’s Selective Silence on Genetics
Why does fitness culture ignore genetics? Simple: it doesn’t sell. If people accepted that their muscle-building potential was largely predetermined, the billion-dollar fitness industry wouldn’t be able to push:
- Expensive training programs promising “X body in X weeks.”
- Supplement stacks claiming to “maximize muscle growth.”
- The illusion that buying a program from a shredded influencer will make you look like them.
Ironically, many of the biggest names in fitness—especially those with extreme physiques—are genetically gifted (and often enhanced by PEDs). Yet, they claim their results come solely from “hard work and dedication,” keeping their followers trapped in a cycle of unrealistic expectations and self-blame.
After nearly 20 years as a personal trainer, I wish I had been more honest about genetics with my clients. Fitness is absolutely a combination of training, nutrition, recovery, and mindset—but genetics are the foundation that determines what’s possible.
Let’s stop pretending everyone can achieve the same results through sheer willpower. Fitness should be about maximizing your individual potential—not chasing an impossible ideal. Focusing on body neutral fitness and strength training gave me tangible, measurable improvements, but it also made me realize how much misinformation circulates in mainstream fitness spaces, particularly in the fitspiration content flooding social media.

Fitspiration: The Reinvention of Beauty Standards
A 2023 study in Computers in Human Behavior compared the effects of fit ideal vs. non-fit ideal body types in fitspiration imagery. The findings? Exposure to fitspiration content significantly increases body dissatisfaction, especially in women who already struggle with self-image. This isn’t surprising—social media’s curated highlight reels create a distorted sense of what’s achievable. And just like 90s diet culture failed to acknowledge genetic differences in weight, today’s fitness culture largely ignores the reality that strength and muscle growth are heavily influenced by genetics.
But the impact of fitspiration goes beyond body image. The same mechanisms that fuel fitness obsession—comparison, idealization, and self-objectification—are also at play in the broader cultural shift toward hypersexualization.
Fitspiration and Self-Objectification: The Internalized Gaze
Self-objectification occurs when a person sees themselves through the eyes of others, measuring their worth by how they look rather than who they are. And nowhere is this dynamic more evident than in fitspiration culture.
John Berger describes this process perfectly in Ways of Seeing:
“A woman must continually watch herself. She is almost continually accompanied by her own image of herself… From earliest childhood she has been taught and persuaded to survey herself continually. And so she comes to consider the surveyor and the surveyed within her as the two constituent yet always distinct elements of her identity as a woman.”
Fitspiration content encourages this exact split identity—one part of a woman is the observer, constantly assessing whether she looks toned, lean, or strong enough. The other part is the observed, existing only as a reflection of an idealized body type. It’s no longer just about fitness; it’s about performing fitness for an audience.
And the consequences are severe:
- Chronic body surveillance leads to increased anxiety, depression, and disordered eating (Fredrickson & Roberts, 1997).
- Instead of focusing on how movement feels, women focus on how their bodies appear while exercising.
- The line between fitness and sexualization blurs, reinforcing the idea that a woman’s body is only valuable when it is desirable to others.
In this way, fitspiration isn’t just a rebranded version of diet culture—it’s also a pipeline to broader cultural hypersexualization, where the body is constantly on display, measured, and objectified. And this feeds directly into an even deeper issue: the normalization of pornography and the sex industry, where women’s bodies are not just idealized but commodified.
By promoting self-objectification as empowerment, fitspiration culture primes women to see themselves as both the product and the consumer, caught in an endless cycle of external validation. And the most insidious part? It’s framed as self-improvement—when in reality, it’s just another system designed to keep women watching themselves instead of living fully.

The Connection Between Fitspiration, Porn Culture, and Self-Objectification
The way women are impacted by pornography—and by extension, the sex industry—is something far too many people overlook. The statistics are staggering:
- The top three porn sites receive a combined 134,491 visits per minute.
- Most pornographic videos contain some form of aggression or violence, particularly toward women. A 2020 meta-analysis found that 88% of pornographic scenes contain physical aggression (slapping, choking, hair-pulling) and 49% contain verbal aggression, with women overwhelmingly being the targets (Bridges et al., 2010).
- Most young people are exposed to pornography between the ages of 11 and 13, with some studies reporting an even earlier age for boys (Wright et al., 2021).
- A 2020 study found that 91.5% of men and 60.2% of women had watched porn in the past month (Solano, Eaton, & O’Leary, 2020).
How This Connects to Fitspiration and Porn Culture
At first glance, fitspiration (or “fitspo”) might seem like it has nothing to do with pornography or the sex industry. After all, isn’t fitness about health and strength? But when we look closer, the connections become clear.
- Both fitspiration and porn culture promote self-objectification.
Fitspiration culture tells women that their worth is tied to their body’s appearance—specifically, whether they have a lean, sculpted, and sexually desirable physique. This reinforces self-objectification, where women begin viewing their bodies primarily as objects to be judged rather than lived-in, experienced, and valued beyond aesthetics.
Remember our study in Computers in Human Behavior (2023) found that exposure to fitspiration imagery leads to increased body dissatisfaction and self-objectification, particularly among women who already struggle with body image….Similarly, pornography fuels external validation as a primary measure of self-worth.
Women in both fitspo and porn culture are expected to conform to an idealized version of femininity that is both hypersexualized and carefully curated for male consumption.
- Both industries capitalize on the illusion of empowerment.
One of the biggest arguments in favor of fitspiration and porn is that they “empower” women. But empowerment, in its truest sense, involves autonomy, agency, and self-determination—not just adhering to societal beauty standards under the guise of “strength” or “choice.”
- Fitspiration content often presents extreme dieting, excessive exercise, and body sculpting as forms of self-discipline and self-improvement, even when they veer into disordered behaviors.
- The porn industry promotes the idea that sex work is a path to empowerment, despite overwhelming evidence of the harm it causes to those involved. Research on women in the porn industry has found high rates of PTSD, substance abuse, and coercion (Farley et al., 2003).
The same narrative that tells women they must be “empowered” by fitspiration also tells them they must be “empowered” by commodifying their bodies through sex work. The reality is that both industries profit from women internalizing external standards of worth rather than defining it for themselves.
- The rise of OnlyFans and the blending of fitness and sex work.
Social media has blurred the lines between fitness influencers and the sex industry in a way that previous generations didn’t experience. Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and OnlyFans have created a new category of influencers who monetize their appearance—whether through fitness content, sexually suggestive photos, or outright pornography.
- Some fitness influencers now have OnlyFans accounts, where they claim to be selling fitness content but also offer sexually explicit material.
- The normalization of “soft porn” in fitness spaces (suggestive poses, hypersexualized workout attire) conditions women to see their fitness journey as something that must be publicly displayed and validated by others.
- Many young women have turned to selling “spicy content” on OnlyFans as a form of income, believing it to be harmless self-expression—only to later experience the psychological and social fallout.
This isn’t just theoretical. A growing body of research shows that women who engage in sexualized self-presentation online report higher levels of self-objectification, body dissatisfaction, and lower self-esteem (Boursier et al., 2020).

The Psychological Toll: What Happens When Women Internalize These Messages?
Self-objectification doesn’t just impact body image—it affects mental health, cognitive performance, and even physical performance. Studies have found that women who are primed to focus on their appearance:
- Perform worse on cognitive tasks (Fredrickson et al., 1998).
- Experience greater body shame and anxiety (Moradi & Huang, 2008).
- Are less likely to engage in activities that prioritize function over appearance (Roberts & Gettman, 2004).
And this has real-world consequences. Women who internalize self-objectification are more likely to experience:
- Higher rates of depression and anxiety
- Greater susceptibility to eating disorders
- Lower confidence in their physical abilities
Reframing the Narrative: What’s the Alternative?
Recognizing these patterns is the first step in breaking free from them. If fitspiration, porn culture, and social media all push the message that women must shape themselves into externally validated objects, then the antidote is reclaiming agency over our bodies—not as things to be looked at, but as tools for living, experiencing, and creating.
- Strength training should be about what your body can do, not how it looks.
- Health and fitness should prioritize function over pain.
- Challenge Beauty Norms & External Validation. Who benefits from women being consumed by their appearance? The more we recognize these influences, the easier it is to resist them.
- Women should be encouraged to pursue movement, sport, and physical strength without the added layer of performative sexuality.
Joan Jacobs Brumberg’s The Body Project reinforced for me how unprepared young women have been for the level of sexualization and exploitation in our culture—something that has only worsened with social media. The way sex work is framed as “empowerment” in some circles ignores the long-term harm it inflicts, and I’ve seen that firsthand.
I can’t wait to discuss this more with my friend Sloane Wilson, a survivor advocate with Exodus Cry, on my podcast later this season. Her insights into the realities of the sex industry and the dangers of normalizing self-objectification are incredibly important for this conversation.